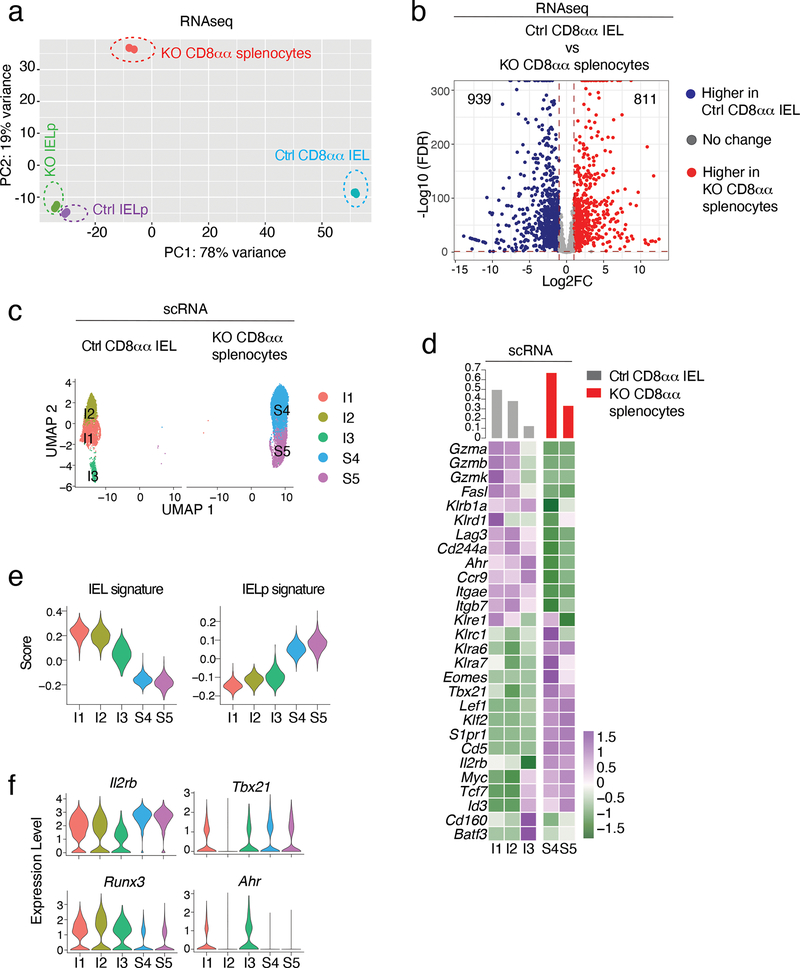
Figure 7. LRF is needed for acquisition of the mature IEL transcriptome.
(a, b) Population RNAseq of Ctrl and KO IELp and CD8αα post-thymic T cells.
(a) PCA plot. (b) Volcano plot showing differentially expressed genes (FDR<0.05, |Log2FC| >1) between Ctrl CD8αα IEL and LRF KO CD8αα spleen T cells. Blue and red symbols indicate genes preferentially expressed in Ctrl and KO cells, respectively. p-value calculated using a Wald test.
(c-f) scRNAseq of Ctrl CD8αα IEL and KO CD8αα spleen T cells. Analyses shown were performed on integrated data from two separate experiments (two replicates per genotype).
(c) UMAP plot, displayed per genotype. Each dot represents a cell and is color-coded by cluster.
(d) Heatmap shows row-standardized expression of selected genes among clusters (below heatmap, color scale at bottom right). For each genotype, the top bar graph indicates the frequency of cells in each cluster relative to the total number of cells with that genotype.
(e) IEL and IELp signature score across clusters from each genotype. The signatures include genes with expression either higher (IEL signature) or lower (IELp signature) in IEL than IELp (FDR <0.01, |Log2FC| >2, Supplementary Table 9).
(f) Violin plots show expression of indicated genes across clusters.