Fig. 10.2.
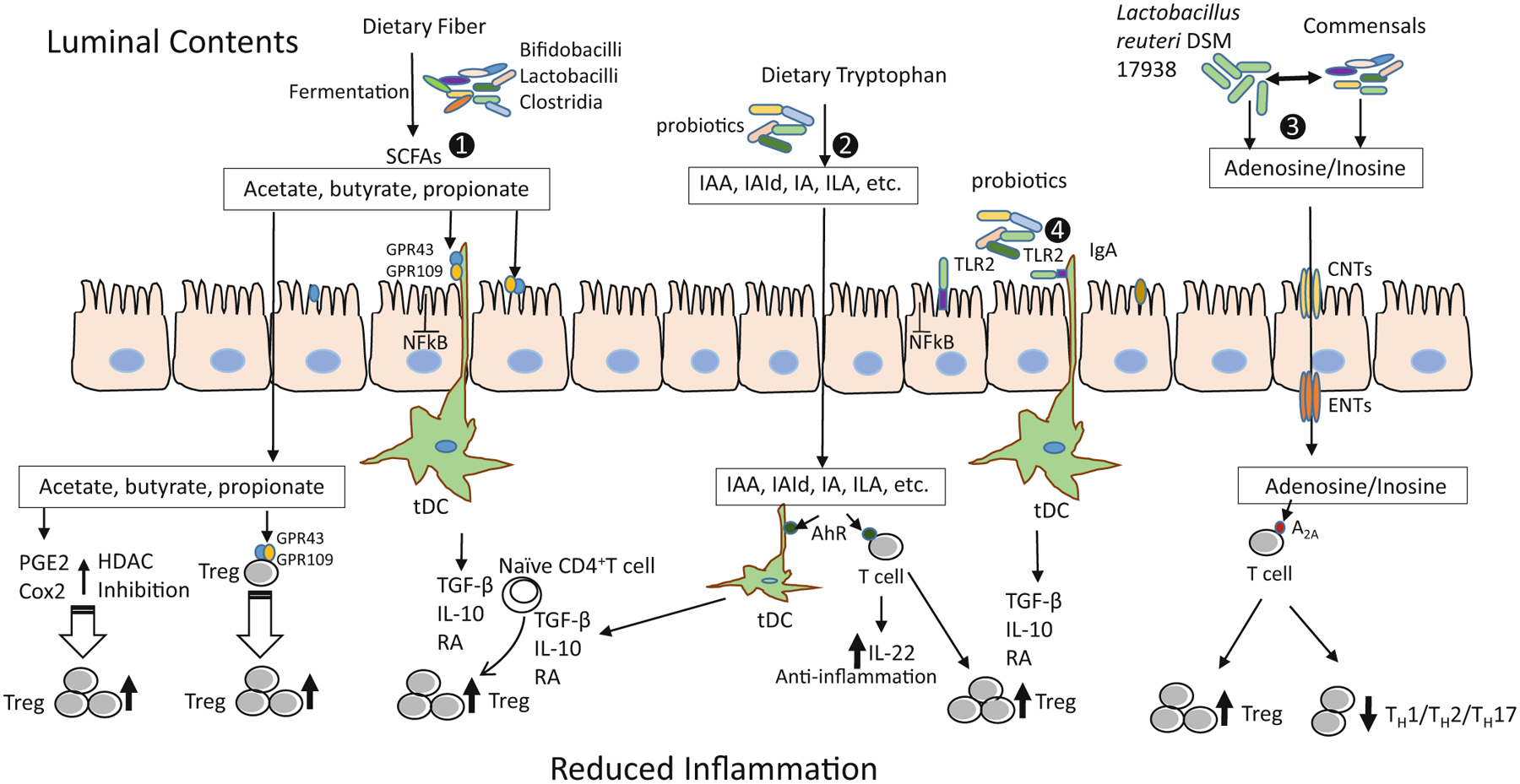
Different mechanisms of Treg induction by probiotics to reduce inflammation. (1) Probiotics metabolize the dietary fibers such as resistant starch, inulin, FOS, β-GOS to release SCFAs: acetate, butyrate and propionate. These SCFAs activate the GPR43 and GPR109A: on intestinal epithelial cells to inhibit the NF-κB pathway to reduce inflammation; on DCs to generate tDCs producing TGFβ, IL-10, and RA; and on Treg cells. This interaction of SCFAs and GPCRs results into induction and expansion of Tregs capable of suppressing the inflammatory state. GPR43 is activated by all three SCFAs; however, GPR109A is activated only by butyrate. SCFA induction also involves inhibition of HDACs which in turn increases the production and suppressive function of FoxP3+Tregs by promoting the acetylation of Foxp3 protein. In addition, SCFAs modulate the production of PGE2 and COX2 (butyrate in particular), promoting expansion of pre-existing Tregs. (2) Microbial tryptophan metabolites including IAA, IAId, IA, and ILA interact with the AHR on DCs to generate tDCs and AHR on T cells to promote Treg function and/or produce anti-inflammatory IL-22. (3) Probiotic Lactobacillus reuteri DSM 17938-mediated production of adenosine and its metabolite inosine, by serving as an A2A agonist, inhibits TH1/TH2/TH17 cells and promotes Treg-mediated immunoregulation. (4) Probiotics interact with TLR2 expressed on intestinal epithelial cells and immune cells to induce tDCs and subsequently to induce Tregs (Illustration by Yuying Liu). Treg regulatory T cell, FOS fructooligosaccharides, GOS galactooligosaccharide, SCFA short-chain fatty acid, NF-κB nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells, DCs dendritic cells, tDCs tolerogenic dendritic cells, GPR43 and GPR109A G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), TGFβ transforming growth factor beta, IL interleukin, RA retinoic acid, HDACs histone deacetylases, PGE2 prostaglandin E2, COX-2 cyclooxygenase-2, IAA indoleacetic acid, IAId indolealdehyde, IA indoleacrylic acid, ILA indolelactic acid, AHR aryl hydrocarbon receptor, A2A adenosine receptor 2A, TH cell T helper cell, TLR2 toll-like receptor 2, CNT concentrative nucleoside transporters, ENT equilibrative nucleoside transporters
