Fig. 5.
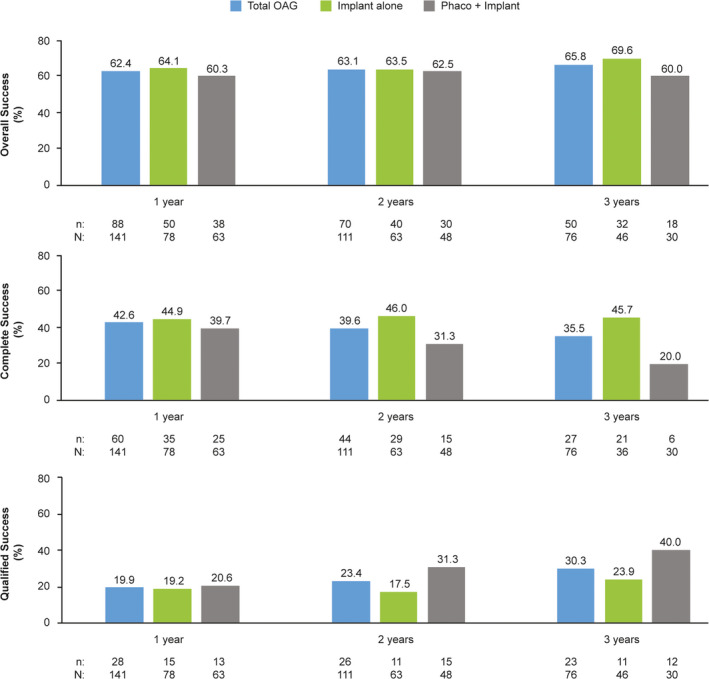
Rates of overall, complete and qualified success at 1, 2 and 3 years postimplantation of the gel stent in the effectiveness OAG population (n = 174)a,b. aAll effectiveness analyses included one eye per patient; in cases of bilateral implantation, only the first implanted eye was analysed. bThis analysis included all patients who had IOP data at baseline. Overall success was defined as the sum of complete success and qualified success. Complete success was defined as ≥20% IOP reduction from medicated baseline without SSI, clinical hypotony (as defined in the Outcomes section) or topical IOP‐lowering medications, analysed in the effectiveness population. Qualified success was defined as ≥20% IOP reduction from medicated baseline without SSI or clinical hypotony while remaining on the same number or fewer topical IOP‐lowering medications, analysed in the effectiveness population, and did not include eyes that met the criteria for complete success. Eyes that required more topical IOP‐lowering medications at years 1 (implant, n = 3; phaco + implant, n = 1), 2 (implant, n = 3; phaco + implant, n = 1) and 3 (implant, n = 2; phaco + implant, n = 2), compared with baseline, were excluded from the success analyses. IOP = intraocular pressure, OAG = open‐angle glaucoma, phaco = phacoemulsification with intraocular lens placement, SSI = glaucoma‐related secondary surgical intervention.
