Figure 4.
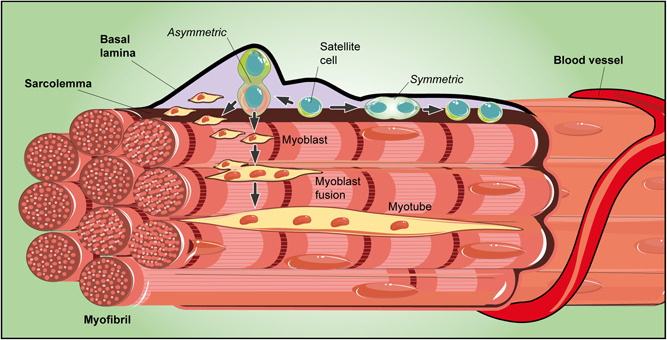
Schematic drawing of a skeletal muscle niche. Satellite cells are small mononucleated cells located between the sarcolemma and the basal lamina. Satellite cells may undergo symmetric or asymmetric division. By symmetric division, two identical progenitor cells are produced, both equally in contact with the sarcolemma and the basal lamina. Otherwise, by asymmetric division, the daughter cell in contact with the basal lamina inherits the role of an uncommitted progenitor, whereas the other, adjacent to the sarcolemma, may undergo myogenic differentiation. Proliferating myoblasts are then produced and, after their fusion, new syncytial contractile muscle cells are assembled
