|
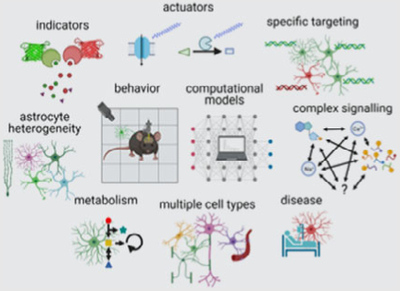
Overall
How do astrocytes integrate and respond to
diverse molecular signals in their extracellular
environment at the cellular and population level? How do they convert this task- and animal
state-dependent information into functional outputs that
modulate neural circuit structure or function on various
temporal and spatial scales? Does this influence on neurons serve
homeostatic functions, augment/complement neural circuit
properties, or both? Do astrocytes perform similar computations in
different brain and spinal cord regions? Do astrocytes temporally hold/store information
and, if so, for what purpose?
|
|
Indicators
What new or improved indicators are needed to
address the above questions (e.g., for neuropeptides,
neuroactive substances, ions, transcriptional processes,
synapse interactions)? How can current limitations to multiplex
measurements be overcome (e.g., indicator
signal-to-noise ratio, spectral variants, interference
with endogenous signaling, buffering effects)?
|
|
Actuators
Given astrocytes’ complex spatiotemporal
signals, how can physiologically meaningful regulation
be achieved? Which approaches allow astrocyte
“inhibition” at high spatial and temporal
resolution? Which astrocyte signaling mechanisms other than
calcium control neural circuit function and animal
behavior on different timescales (e.g., K+,
Na+, cAMP)?
|
|
Genetic targeting approaches
|

|
Behavioral assays
How can quantitative behavioral assays be used
to understand better astrocyte signal integration in
vivo (e.g., noradrenergic, cholinergic, and dopaminergic
signaling)? How can these assays be used to uncover
astrocyte effects on neural circuit function in vivo
(e.g., leveraging astrocytes’ refractory
period-dependent excitation)?
|

|
Computational approaches
What molecular, structural, or gene expression
changes should be measured to understand better
astrocytes’ signal integration (with existing or
novel indicators)? How do astrocytes control (directly or
indirectly) neural circuit properties on various spatial
and temporal scales (e.g., spike frequency, synchrony,
oscillations, excitation-inhibition balance)? How is astrocytes’ structural and
functional heterogeneity relevant to neural circuit
operation? How can modeling help predict circuit functions
of astrocytes unique to humans?
|
|
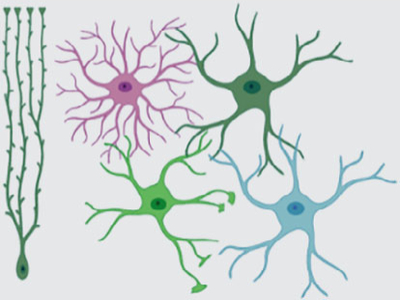
Astrocyte heterogeneity
How does astrocyte heterogeneity at the
synaptic, cellular, circuit, and systems levels
influence neural circuit function? What intrinsic and environmental factors
determine this heterogeneity in health and disease?
|
|
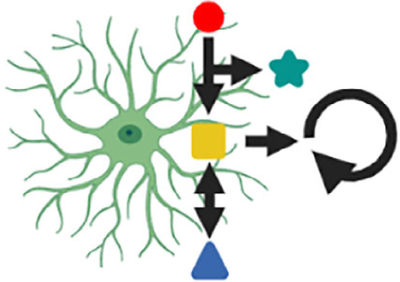
Astrocyte metabolism
How do astrocyte-derived metabolites (e.g.,
lactate) regulate neural circuit function and animal
behavior? How does altered metabolism in astrocyte-neuron
assemblies influence neural circuit function and animal
behavior?
|
|
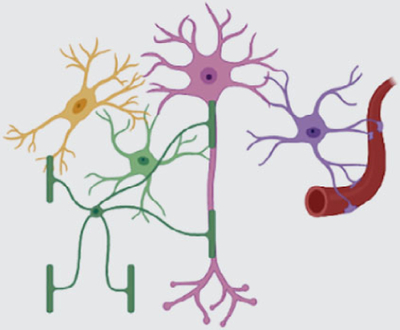
Contribution of other non-neuronal
cells
To what extent does astrocyte modulation of
neural circuit function rely on other non-neuronal
cells? How do these cells modulate astrocyte-neuron
communication in health and disease? How do these cells influence neuronal circuit
function directly?
|
|
Disease
|










