FIG 2.
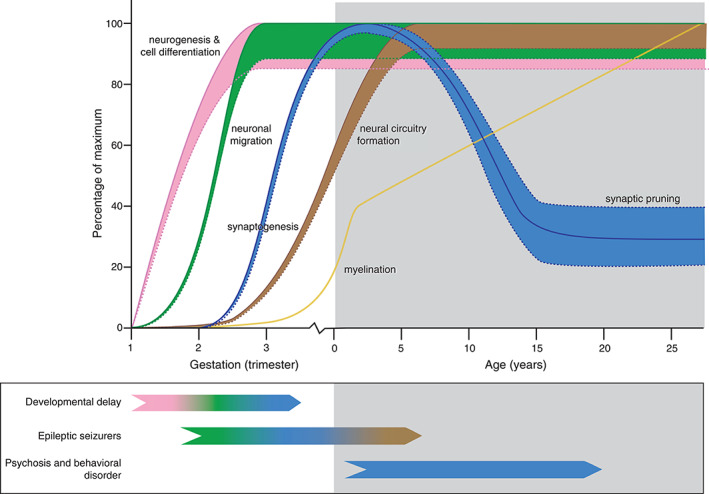
Model for potential effects of mutant huntingtin (mHTT) in the developing brain of juvenile‐onset Huntington disease (JHD) patients. Normal brain development involves overlapping processes of neurogenesis and cell differentiation (pink line), neuronal migration (green line), neural circuitry formation by dendrite branching (brown line), and synaptogenesis (first part of blue line), followed by selective synaptic pruning (second part of blue line) and myelination (yellow line). Straight lines represent physiological brain development, dotted lines potentially altered neurodevelopment due to a dosage effect of CAG repeat length or interplay with brain maturation in JHD patients. Distinct clinical characteristics in JHD patients include developmental delay, epileptic seizures, psychosis, and behavioral disorders that could relate to various defects in neurodevelopment or brain maturation (see color code of the representative lines). Note the potential bidirectional effect on synapse abundance (blue dotted lines) on developmental delay (associated with impaired prenatal synaptogenesis) and psychosis and behavioral disorders (associated with impaired postnatal synaptic pruning). [Color figure can be viewed at wileyonlinelibrary.com]
