Figure 1.
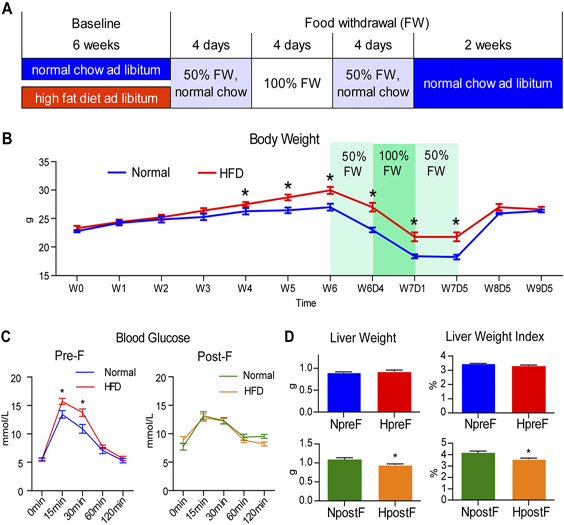
Experimental outline and the effects of food withdrawal on body weight, liver weight, and glucose tolerance. A) Outline of animal treatments, which consisted of a 6‐wk ad libitum normal chow (for normal mice) or HFD (for obese mice) treatment at baseline, a 4‐d 50% food withdrawal (FW) with normal chow, a 4‐d complete FW, another 4‐d 50% FW with normal chow, and a 2‐wk recovery with ad libitum access to normal chow. The end of the 6‐wk baseline treatment was defined as the pre‐food withdrawal time point, and the end of the 2‐wk recovery was defined as the post‐food withdrawal time point. B) Body weight of the normal and HFD groups throughout the experiment. C) The blood glucose levels during the OGTT (0, 15, 30, 60, and 120 min postloading) of the animals in the normal and HFD groups before and after food withdrawal. D) Liver weight and liver weight index (liver weight/body weight × 100) of the animals in the normal and HFD groups before and after food withdrawal. Data are expressed as means ± sem. Group differences were assessed by using the Mann‐Whitney U test. *P < 0.05 when comparing normal and HFD groups.
