Figure 4.
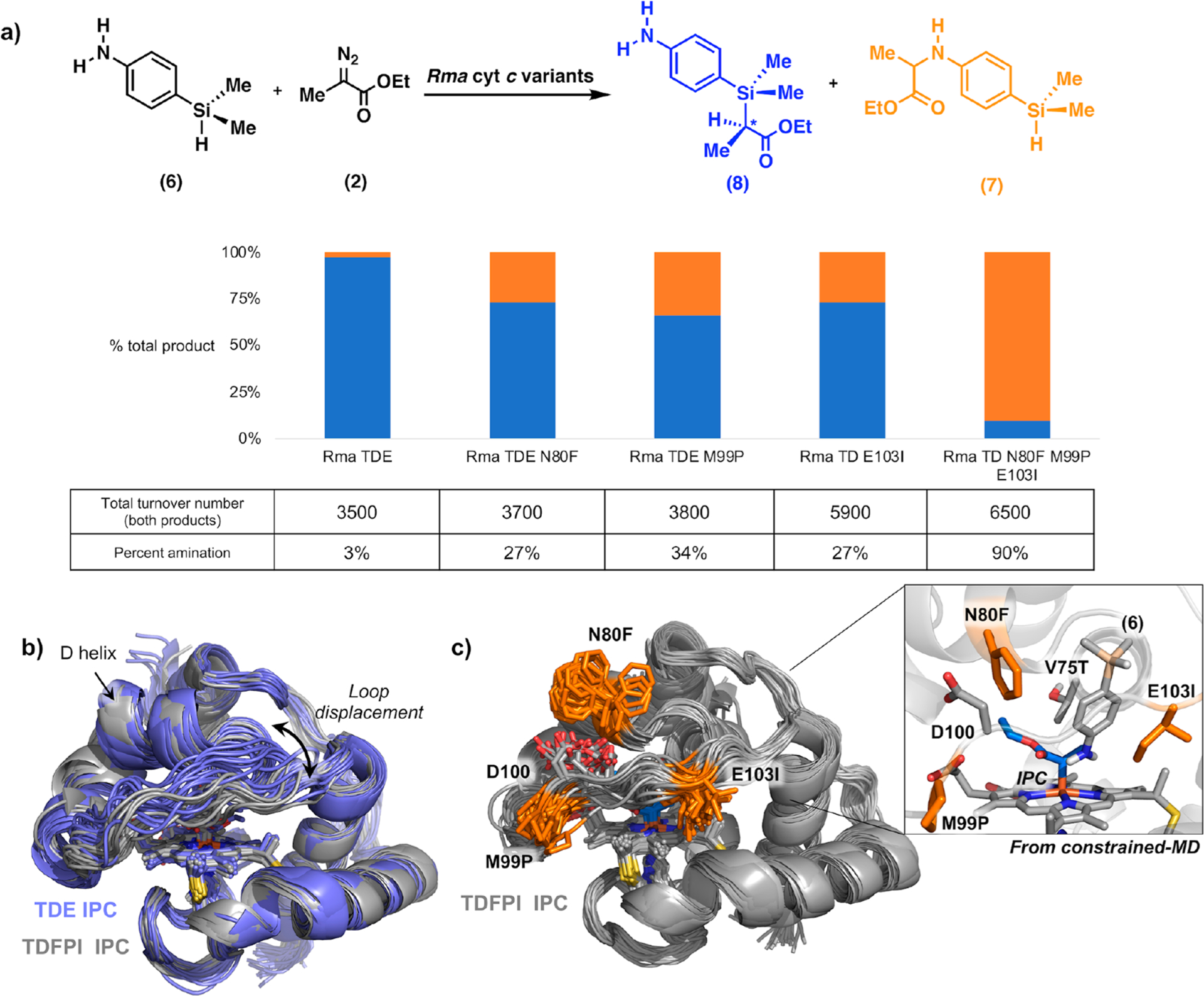
(a) Site saturation mutagenesis of Rma TDE for chemoselective amination over Si–H carbene insertion using p-dimethylsilylaniline 6 and diazo compound 2. Reactions were performed with heat-treated cell lysates with 1 μM Rma cyt c protein, 10 mM 6, 10 mM 2, and 10 mM sodium dithionite in M9-N buffer. Chemoselectivity was measured as the percent of amination product over total product formed and was determined by gas chromatography. Total turnover number (TTN) is defined as the combined concentration of 7 and 8, over protein concentration. See Supporting Information for full description of the experimental procedures. (b) Overlay of different snapshots obtained from 500 ns MD trajectories of Rma TDE (purple) and Rma TDFPI (gray) IPC-bound complexes. The most important structural changes correspond to the preferred “top-open” conformation adopted by the front loop (residues 98–103) in Rma TDFPI as compared to the parent Rma TDE variant. (c) Overlay of snapshots obtained from 500 ns MD trajectory for Rma TDFPI IPC-bound complex. The mutations N80F, M99P, and E103I are highlighted in orange. Inset: Snapshot from constrained-MD simulation of Rma TDFPI IPC-bound complex with substrate 6, showing how substrate 6 prefers to adopt a binding pose that favors amination via N-nucleophilic attack.
