Fig. 6.
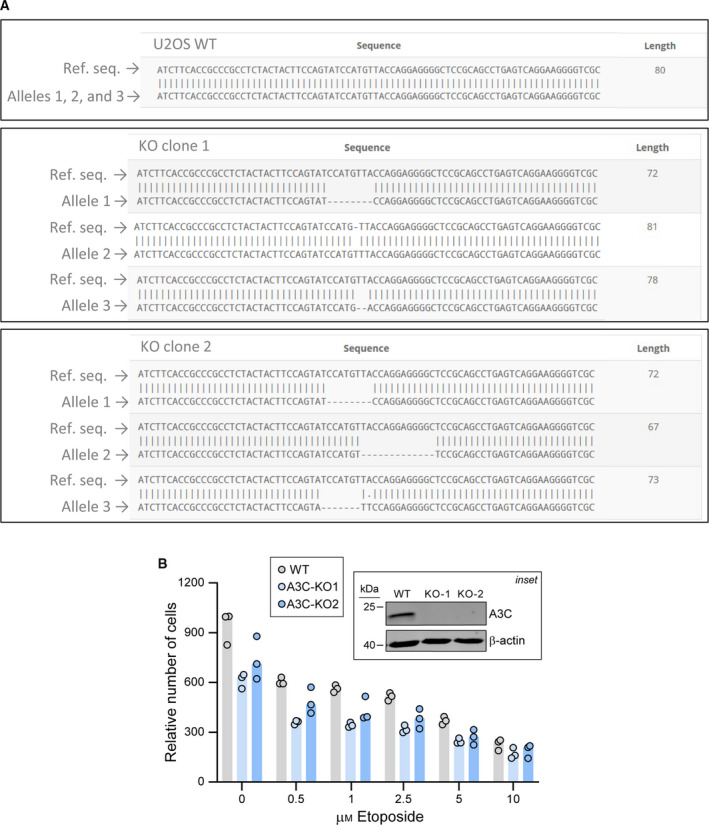
CRISPR/Cas9‐mediated A3C gene disruption and its impact on etoposide sensitivity. (A) A3C gene sequencing in wild‐type (WT) and two CRISPR/Cas9‐generated A3C knockout U2OS cells (KO1 and KO2). The presence of frameshift mutations located in the vicinity of the sgRNA target site was detected in the three A3C alleles of the knockout clones. (B) Wild‐type (WT) and A3C knockout (KO) U2OS cells were seeded in 12‐well plates and treated with increasing concentrations of etoposide for 72 h. The relative number of cells was determined by Presto‐Blue assay. Inset: the presence of A3C protein in these cells was evaluated by western blotting. The cells were stimulated with 5 μm etoposide for 48 h to boost A3C expression.
