FIGURE 1.
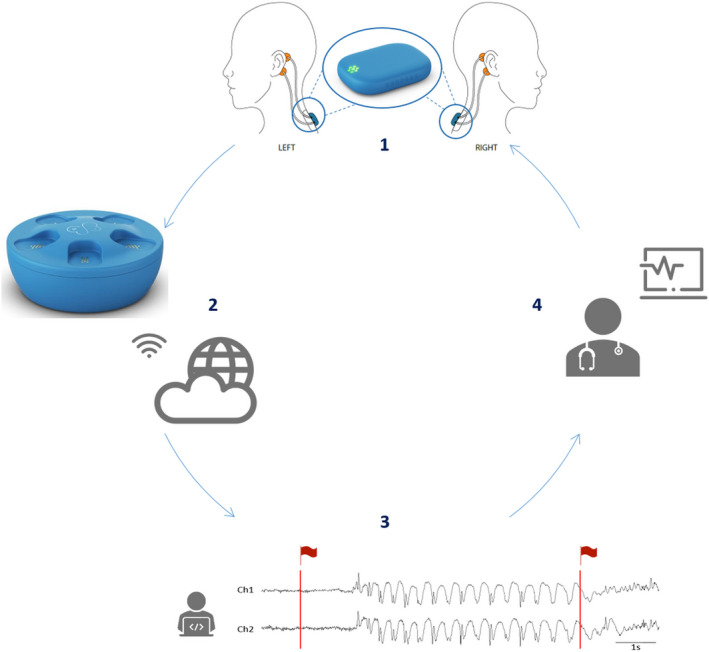
Concept of the Sensor Dot (SD) used as a wearable to detect absence seizures. (1) Four electrodes (in orange) are placed behind the ears of the patient and connected to the mobile electroencephalographic (EEG) device, the SD, which is attached to the upper back via an adhesive (in blue). An enlarged image of the SD is given in the circle. (2) After 24 h of recording, the SD is placed in the docking station, which allows recharging of the battery. In addition, when the SD is in the docking station, the SD EEG data are automatically uploaded to the cloud via a Wi‐Fi connection. (3) Afterward, the absence detection algorithm analyzes the data and flags segments of interest (in red). (4) Finally, the flagged data are sent back to the treating neurologist, who can then review the flagged SD EEG data in a short time.
