FIGURE 5.
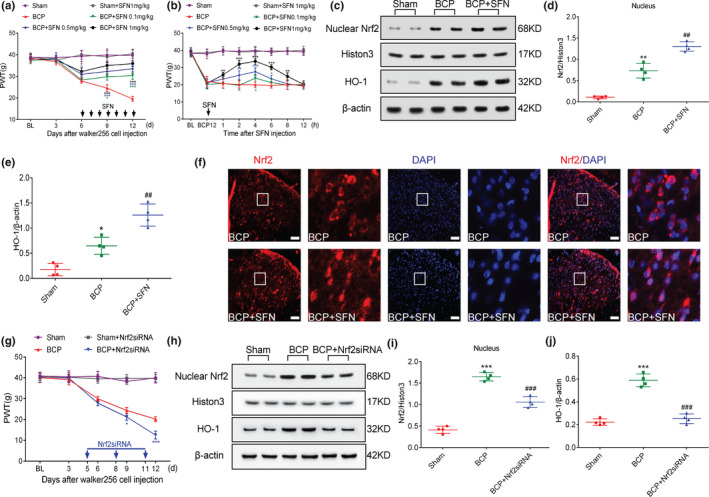
Nuclear factor erythroid 2 (NFE2)‐related factor 2 (Nrf2) nuclear transcription is associated with the development of pain behaviour in rats with bone cancer pain (BCP). (a, b) Intrathecal administration of sulforaphane (SFN) reduced hyperalgesia in rats with BCP in a dose‐dependent manner(*p < .05, ***p < .001 vs. BCP group; n = 6, two‐way repeated‐measures ANOVA). (c–e) Rats were killed on BCP 12 days to collect spinal cord tissue. Western blot analysis showed that SFN further promotes the expression of Nrf2 nucleoprotein (c and d) and its downstream target protein heme oxygenase‐1 (HO‐1) (c and e) (*p < .05, **p < .01 vs. sham group; ## p < .01 vs. BCP group; n = 4, one‐way ANOVA). (f) Double immunolabelling showed that Nrf2 was almost completely localized in the nucleus after treatment with SFN. High magnification images of immunofluorescence are shown in the white box. Lumbar enlargements were collected on day 12 after tumour inoculation; n = 4. Scale bar: 50 μm. n represents the number of experimental animals in each group. (g) Intrathecal injection of Nrf2 siRNA at 5, 8 and 11 days after the operation significantly induced hyperalgesia in rats with BCP (*p < .05, ***p < .001 vs. BCP group; n = 6, two‐way repeated‐measures ANOVA). (h–k) Rats were killed 12 days after the operation to obtain spinal cord tissue for western blot analysis. Western blot analysis showed that Nrf2 siRNA treatment significantly inhibited BCP‐induced Nrf2 nucleoprotein and HO‐1 expression(***p < .001 vs. sham group; ### p < .001 vs. BCP group; n = 4, one‐way ANOVA)
