FIGURE 8.
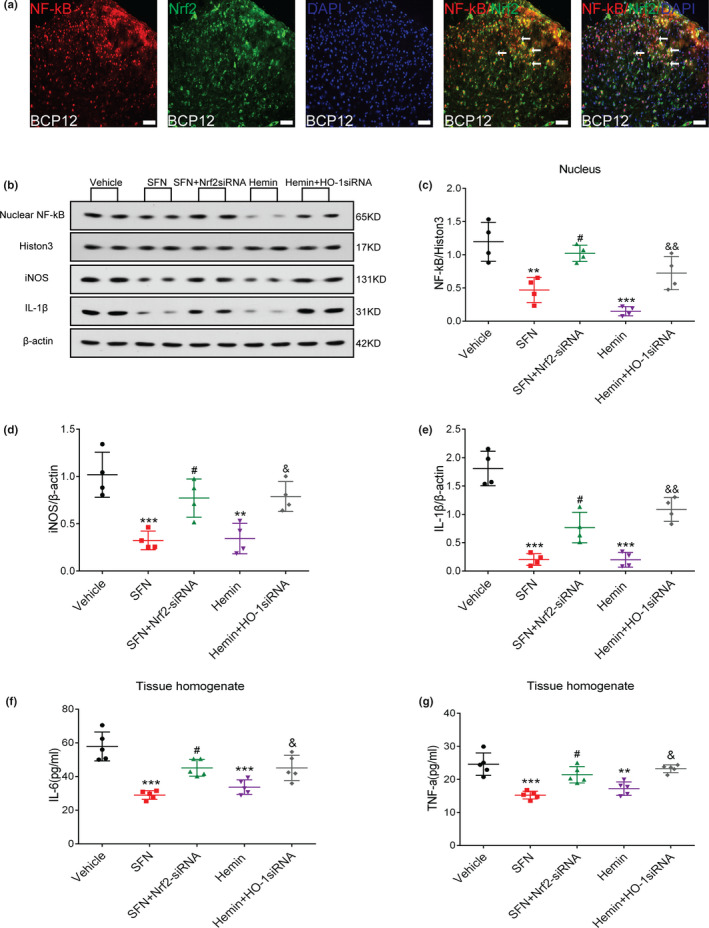
The nuclear factor erythroid 2 (NFE2)‐related factor 2 (Nrf2)/heme oxygenase‐1 (HO‐1) axis is involved in the regulation of the nuclear factor‐kappa B (NF‐κB) signalling pathway in the spinal cord of rats with bone cancer pain (BCP). (a) NF‐κB (red) and Nrf2 (green) were coexpressed in the dorsal horn of the spinal cord of rats with BCP. Sections were counterstained with DAPI (blue) to label cell nuclei. The white arrows show colocalization of NF‐κB with Nrf2. Lumbar enlargements were collected on day 12 after tumour inoculation; n = 4. Scale bar: 50 μm. (b–g) Treatment with an Nrf2 agonist (sulforaphane, SFN) and HO‐1 agonist (hemin) significantly inhibited the activation of NF‐κB and the release of downstream inflammatory factors in the spinal cord of rats induced by BCP. Combined intrathecal administration of siRNA reversed this inhibitory effect. Rats were killed after 12 days of BCP to collect spinal cord tissue. Western blotting was employed to detect the expression of NF‐κB nuclear protein and inflammatory factors (inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) and interleukin‐1beta (IL‐β)) in the spinal cord of rats with BCP after different treatments (b–e) (**p < .01,***p < .001 vs. vehicle treatment group; # p < .05 vs. SFN treatment group; & p < .05, && p < .01 vs. hemin treatment group; n = 4, one‐way ANOVA). Enzyme‐linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) was used to detect the expression of inflammatory factors, tumour necrosis factor‐alpha (TNF‐α) and interleukin‐6 (IL‐6) (f and g) (**p < .01,***p < .001 vs. Vehicle treatment group; # p < .05 vs. SFN treatment group; & p < .05 vs. hemin treatment group; n = 5, one‐way ANOVA). n represents the number of experimental animals in each group
