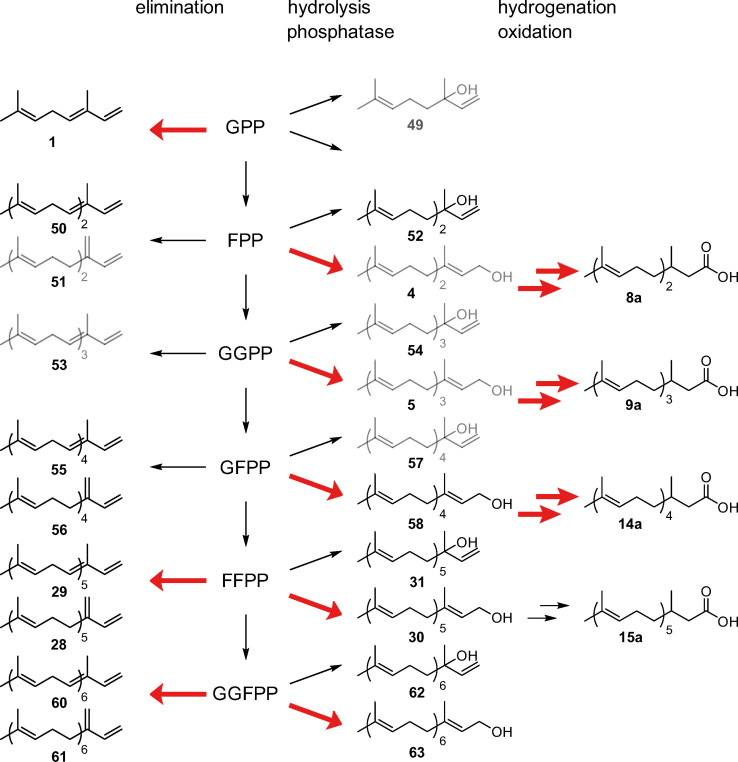
Figure 10.
Biosynthesis of terpenes in H. erato. Major pathways are indicated by red arrows and minor components of the CSG secretion are shown in grey. Typical terpene elongation takes place from geranyl pyrophosphate (GPP) via farnesyl pyrophosphate (FPP) to geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate (GGPP). Further elongation is performed by unusual enzyme activity leading to geranylfarnesyl pyrophosphate (GFPP), farnesylfarnesyl pyrophosphate (FFPP), and geranylgeranylfarnesyl pyrophosphate (GGFPP). Elimination leads to α‐ and β‐terpene hydrocarbons, whereas hydrolysis delivers alcohols of the nerolidol (54) type. A phosphatase furnishes terminal alcohols that will be in turn further modified by hydrogenation and oxidation to form dihydroterpene acids, precursors of the CSG esters.