Figure 1.
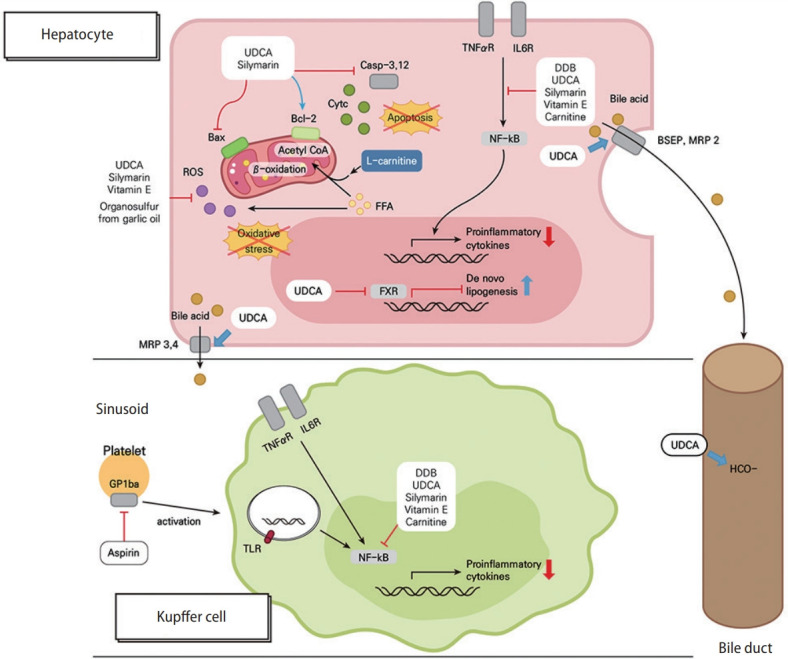
Mechanisms for protective effects by UDCA, silymarin, DDB and its combination with other supplements, vitamin E, and aspirin in chronic liver diseases. UDCA and silymarin negatively regulate the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway by inhibiting Bax translocation, reinforcing Bcl-2 activity, and blocking the activations of caspase-3 and -12, which prevents the apoptosis of hepatocytes in chronic liver diseases. Moreover, UDCA, silymarin, vitamin E, and organosulfur (from garlic oil) relieve ROS-mediated oxidative stress in hepatocytes. Cytosolic FFA contributes to the intracellular ROS pool, and carnitine shuttles FFA-derived acyl-coenzyme as into the mitochondria, making them to undergo β-oxidation. TNF-α/IL-6 receptor signaling and TLR signaling upregulates the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines via NF-κB activation, while UDCA, silymarin, DDB, vitamin E, and carnitine block this pathway in both hepatocytes and Kupffer cells. UDCA increases the secretion of bile acids via the upregulation of the hepatobiliary transporter genes, such BSEP, MRP2, and MRP3, and also enhances biliary bicarbonate excretion. Interestingly, UDCA induces neutral lipid accumulation in hepatocytes by exerting FXR-antagonistic effects. Aspirin attenuates intrahepatic inflammation by blocking platelet-derived, GPIbα-mediated Kupffer cell activation. UDCA, ursodeoxycholic acid; MRP, multidrug resistance protein; ROS, reactive oxygen species; Bcl-2, B-cell lymphoma 2; FFA, free fatty acid; FXR, farnesoid X receptor; TNF, tumor necrosis factor; IL-6; interleukin-6; DDB, dimethyl-4,4’-dimethoxy-5,6,5’,6’-dimethylenedixoybiphenyl-2,2’-dicarboxylate; NF-κB, nuclear factor kappa-B; BSEP, bile salt export pump; GP1bα, glycoprotein 1bα; TLR, toll-like receptor.
