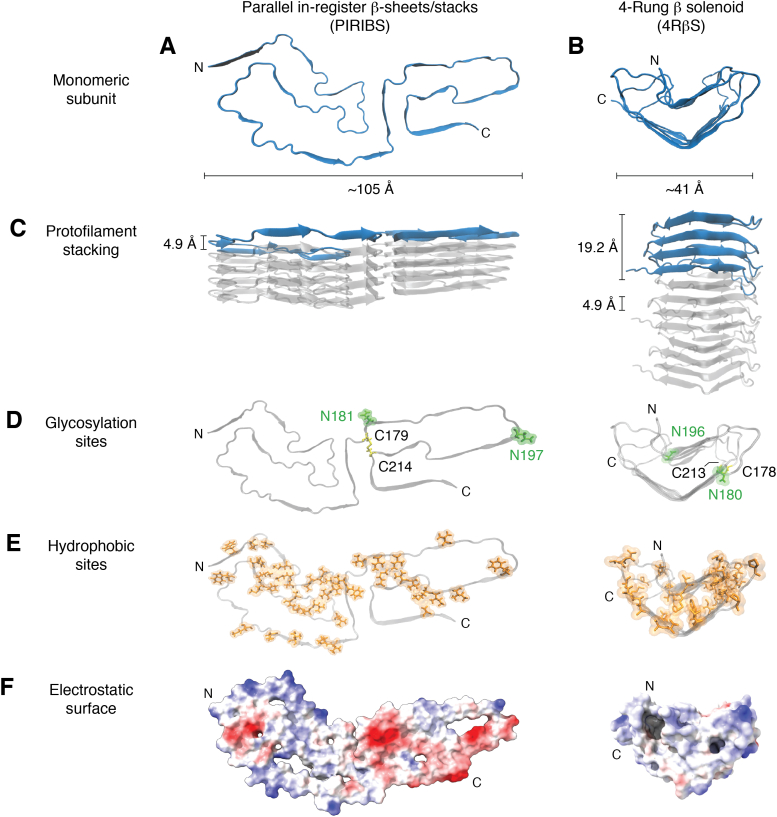
Figure 1.
Recent models for prion fibrils.A, monomeric subunit of the 263K prion within its parallel in-register intermolecular β-sheet or stack (PIRIBS) architecture (38, 39). B, monomeric subunit within a 4-rung β-solenoid (4RβS) architecture hypothesized initially for the anchorless RML (aRML) prion (50), but see contrary data demonstrating PIRIBS architecture for this strain (41). Spacing of cross-β strands in both models is ∼4.9 Å (C). This is also the spacing of each monomer in the PIRIBS structure, whereas in the 4RβS model the monomers span 19.2 Å along the fibril axis (C). Glycosylation sites (D) at positions N181 and N197 (hamster numbering, PIRIBS) and N180 and N196 (mouse numbering, 4RβS) are labeled in green and a disulfide bond between C179 and C214 (PIRIBS) and C178 and C213 (4RβS) is colored in yellow. Note: an extra glycine residue at position 53 in the hamster PrP sequence shifts the hamster-mouse sequence alignment for subsequent residues. The lower panels show the distribution of hydrophobic residues in orange (E) and the electrostatic surface (F) (red and blue indicate negative and positive charges, respectively).