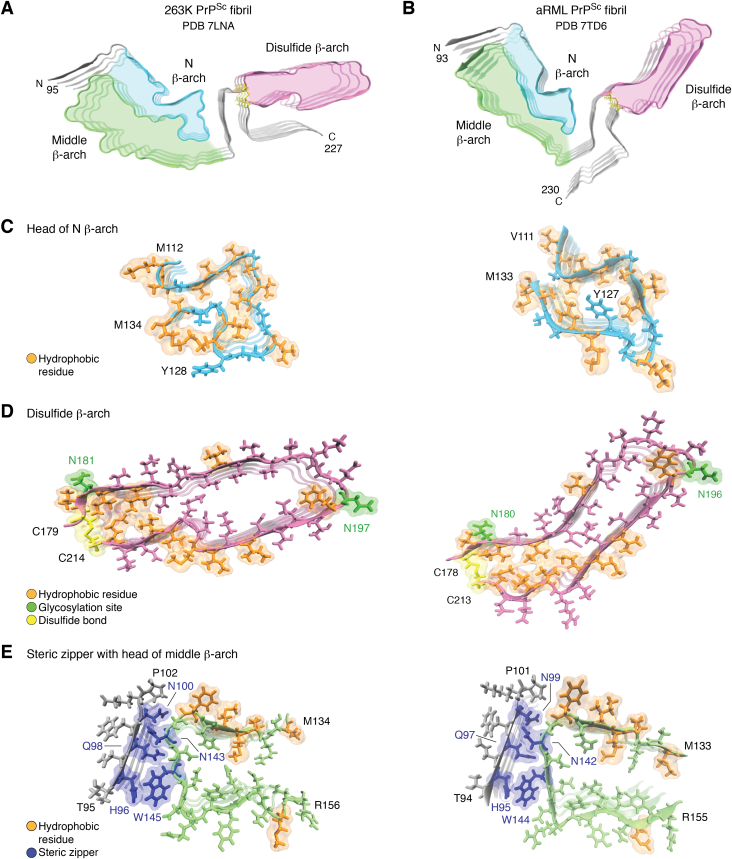
Figure 3.
Comparison of 263K and aRML prion structures. Cross-sections of the (A) 263K and (B) aRML fibril (4-monomer segments) highlighting analogous β-arch motifs (N β-arch, cyan; middle β-arch, green; disulfide β-arch, pink). C, tips of N β-arches of 263K (left) and aRML (right) with hydrophobic residues in orange. D, disulfide β-arches (pink) with respective disulfide bonds (yellow), glycosylation sites (green), and hydrophobic residues (orange). E, steric zippers (blue) formed between tips middle β-arches and respective N-terminal residues. The 263 K structure illustrated in this figure includes residues 194 to 196 which were not specified in PDB ID 7LNA. aRML, anchorless RML; PDB, Protein Data Bank.