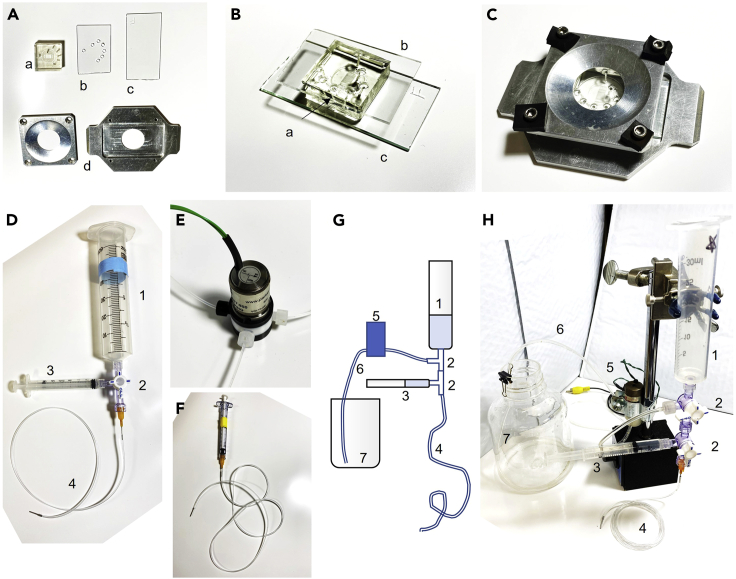
Figure 3.
Microfluidic setup
(A) Pictured are the neural imaging microfluidic device (a), the drilled top glass piece (b), the hydrophobic bottom glass piece (c), and the metal device holder (d).
(B) The microfluidic device is sandwiched between top and bottom glass pieces.
(C) Device secured in a clamp.
(D) Microfluidic reservoir constructed from a 60 mL syringe for fluid storage (1), 3-way Luer valve for reservoir control (2), a 3 mL syringe for fluid priming (3), and tubing (4).
(E) Three-way actuated fluidic valve for switching between flows during the automated neural imaging trials.
(F) Worm loading syringe.
(G and H) Schematic and photo of the outflow assembly consisting of a fluid reservoir (1), two Luer valves (2), a priming syringe (3), tubing to the device (4), the outflow pinch valve (5), tubing to waste (6), and a waste container (7).