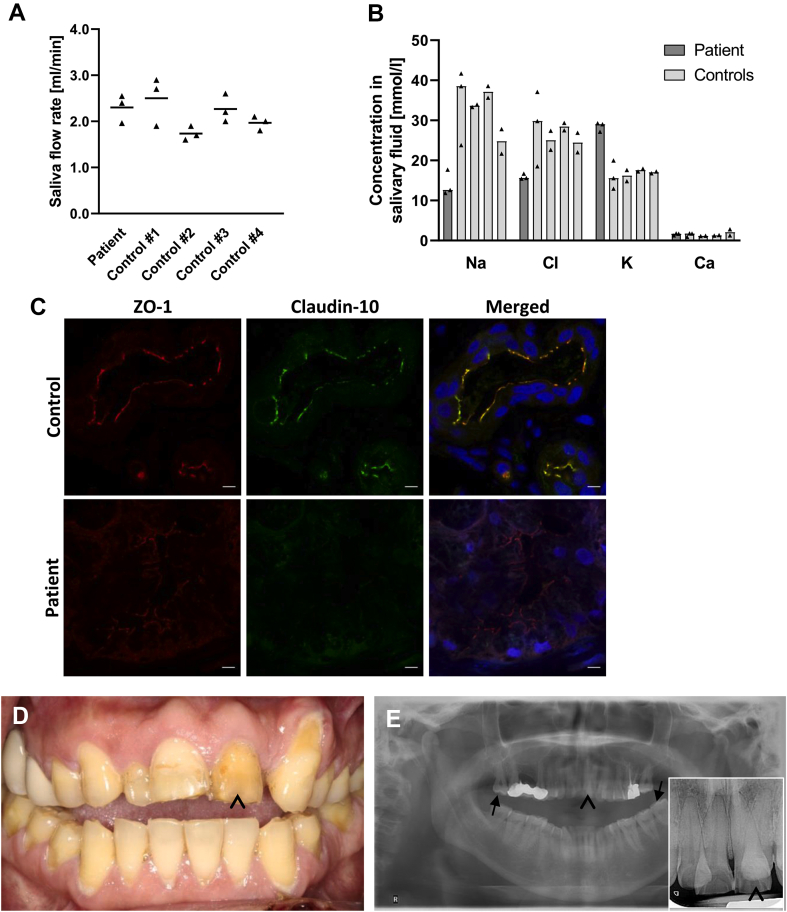
Figure 2.
Assessment of dental phenotype and saliva secretion. (A) Stimulated saliva flow rates in the patient and in 4 control subjects. The amount of saliva produced did not differ between the patient and controls. Mean. (B) Assessment of Na+, Cl−, K+, and Ca2+ concentrations in salivary fluid from the patient and from 4 control subjects. While Na+ and Cl− concentrations were markedly lower in the patient, K+ levels were exceedingly high. Ca2+ concentrations turned out to be comparable between the patient and control subjects. Median. (C) Immunofluorescence labeling of claudin-10 and ZO-1 in submucosal salivary glands from the labial mucosa. When compared with control tissue, a complete absence of claudin-10 and a weaker ZO-1 signal are evident in the patient. Nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue). Scale bars, 5 μm. (D,E) Dental findings in the patient. Both clinical view and radiographs demonstrate severe enamel wear of the permanent teeth especially in the anterior region (arrowheads). Note the anteriorly open bite which is frequently associated with amelogenesis imperfecta41 and makes enamel wear unlikely to result from bruxism. On radiographs, enamel is still evident on molar teeth (arrows).