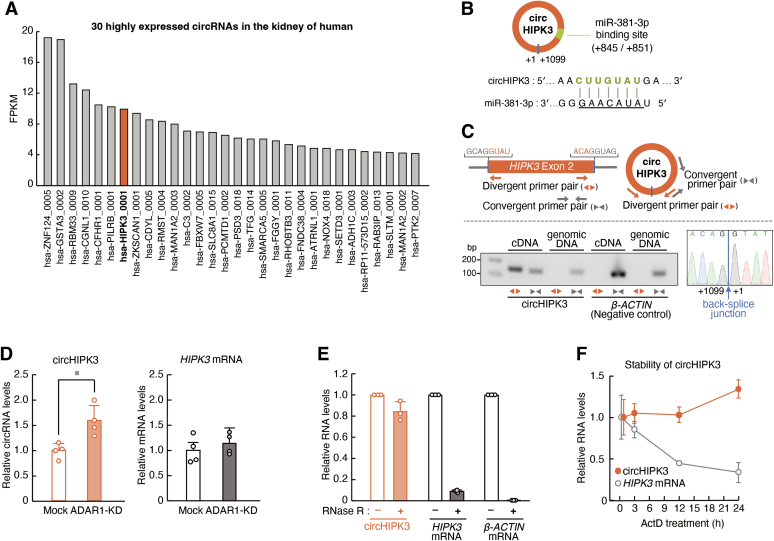
Figure 3.
ADAR1 regulates the expression of circHIPK3 in RPTECs.A, 30 highly expressed circRNAs in the human kidney registered in circAtlas database. FPKM: fragments per kilobase of exon per million mapped reads. B, schematic diagram showing the putative target site of miR-381-3p in circHIPK3. The interaction of miR-381-3p and the circRNAs was predicted using starBase v2.0. C, validation of circHIPK3 detection by RT-PCR. Divergent primers amplified the circHIPK3 back-splice junction sequence in the cDNA but not the genomic DNA. Convergent primers amplified both mRNA in cDNA and genomic DNA. Sanger sequencing confirmed the back-splice junction sequence of the PCR products with the divergent primers (right panel). D, the expression levels of circHIPK3 and HIPK3 mRNA in mock-transduced and ADAR1-KD RPTECs. The expression levels were normalized to those of 18S rRNA. Values are the mean with SD (n = 4). ∗p < 0.05; significant difference between the two groups (t6 = 3.494, p = 0.013 for circHIPK3; unpaired t test, two sided). E, qRT-PCR analysis for the abundance of circHIPK3, HIPK3 mRNA, and β-ACTIN mRNA in RPTECs treated with RNase R. The amounts of target RNAs were normalized to those in the mock treatment. F, the stability of circHIPK3 and HIPK3 mRNA in RPTECs. Cells were treated with 5 μM actinomycin D (ActD), and RNA was extracted at the indicated time points. The expression levels were normalized to those of 18S rRNA. Values are the mean with SD (n = 4).