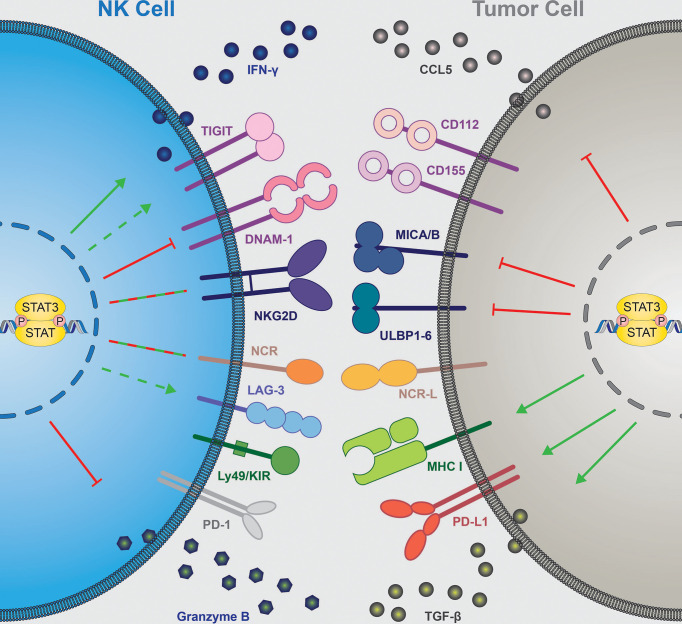
Figure 2.
STAT3 contribution to NK cell-mediated tumor immune surveillance. NK cell-intrinsic STAT3 (left) inhibits expression of granzyme B and DNAM-1 ( ), increases IFNγ secretion (
), increases IFNγ secretion (
 ) and seems to upregulate TIGIT and LAG-3 (
) and seems to upregulate TIGIT and LAG-3 ( ), while the effect on NCRs and NKG2D expression remain context dependent (
), while the effect on NCRs and NKG2D expression remain context dependent ( ). Tumor cell-intrinsic STAT3 (right) inhibits expression of NKG2D ligands (MICA/B, ULBPs) and NK-cell attracting chemokine CCL5 (
). Tumor cell-intrinsic STAT3 (right) inhibits expression of NKG2D ligands (MICA/B, ULBPs) and NK-cell attracting chemokine CCL5 ( ). STAT3 in tumor cells upregulates surface expression of MHC I and PD-L1 molecules and secretion of immune suppressive TGF-β (
). STAT3 in tumor cells upregulates surface expression of MHC I and PD-L1 molecules and secretion of immune suppressive TGF-β (
 ). NK, natural killer; IFN, interferon; DNAM-1, DNAX accessory molecule; NKG2D, NK-cell receptor natural killer group 2D; NCR, natural cytotoxicity receptor; KIR, killer-cell immunoglobulin-like receptor; CCL5, C-C motif chemokine ligand 5; CD, cluster of differentiation; MICA/B, major histocompatibility complex class I-related sequence A/B; ULBP, UL16-binding protein; MHC I, major histocompatibility complex I; TGF-β, transforming growth factor β, STAT, signal transducer and activator of transcription. TIGIT, T cell immunoreceptor with Ig and ITIM domains; LAG-3, lymphocyte-activation gene 3; PD-(L)1, programmed cell death ligand/protein 1.
). NK, natural killer; IFN, interferon; DNAM-1, DNAX accessory molecule; NKG2D, NK-cell receptor natural killer group 2D; NCR, natural cytotoxicity receptor; KIR, killer-cell immunoglobulin-like receptor; CCL5, C-C motif chemokine ligand 5; CD, cluster of differentiation; MICA/B, major histocompatibility complex class I-related sequence A/B; ULBP, UL16-binding protein; MHC I, major histocompatibility complex I; TGF-β, transforming growth factor β, STAT, signal transducer and activator of transcription. TIGIT, T cell immunoreceptor with Ig and ITIM domains; LAG-3, lymphocyte-activation gene 3; PD-(L)1, programmed cell death ligand/protein 1.