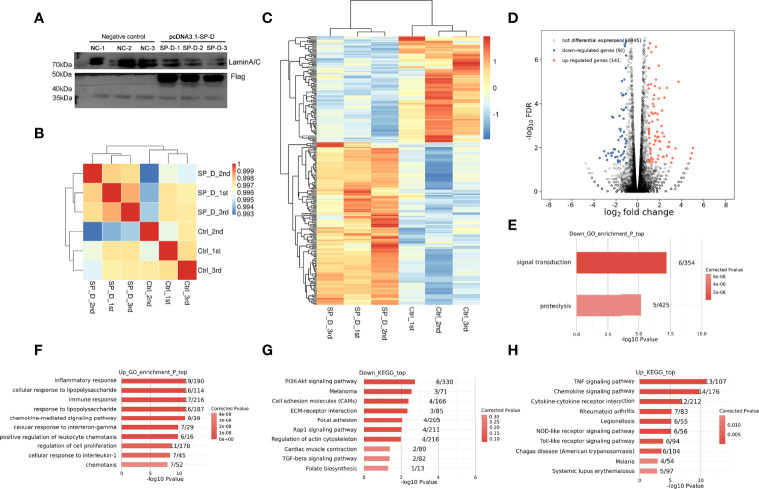
Figure 1.
Effects of SP-D overexpression on the gene expression profile of chondrocytes. (A) Chondrocytes were co-treated by lipofectamine transfected pcDNA3.1 empty plasmid and pcDNA3.1-SP-D plasmid (1 μg/μL). The protein expression of SP-D was assessed via western blotting. (B) The clustering analysis of samples showed high similarity, which confirmed the correctness of the experimental design and sample sampling. (C) The heat map showed that the gene expression patterns and clustering relationships of the samples were similar. (D) Comparisons between samples showed the number of differentially expressed genes. (E, F) GO analysis showed that the biological processes such as regulation of ‘inflammatory responses’, ‘immune response’ and ‘response to LPS’ were associated with SP-D in chondrocytes. (G, H) KEGG pathway analyses revealed these genes to be significantly linked to pathways including the ‘PI3K-Akt signaling pathway’, ‘ECM-receptor interaction’, ‘TLR signaling pathway’, and ‘TNF signaling pathway’.