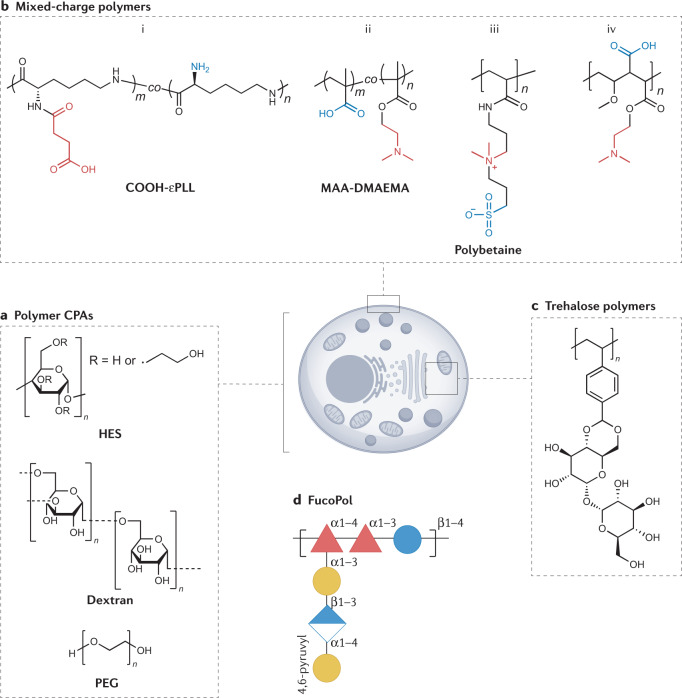
Fig. 4. Macromolecular cryoprotectants for cryopreservation.
There is a huge interest in using macromolecular cryoprotectants to mimic the action of antifreeze proteins, as well as investigate new methods of protection during cold temperature exposure. This started with the use of polymers such as hydroxyethyl starch (HES), dextran and poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) (a). More recently, polyampholytes (polymers with alternating positive and negative charges) have been shown to be beneficial for cryopreservation of mammalian cells, such as bi (ref.88), bii (ref.91) and biv (ref.98). Their modes of action are still being elucidated, but may involve membrane stabilization and ion trapping. Polybetaines (biii) with mixed charges on the same polymer branch have, so far, not shown the same benefit95. Alternative macromolecular structures that are of interest for cryopreservation include those with trehalose side chains (c)102,103 and FucoPol (d)106. CPAs, cryoprotective agents.