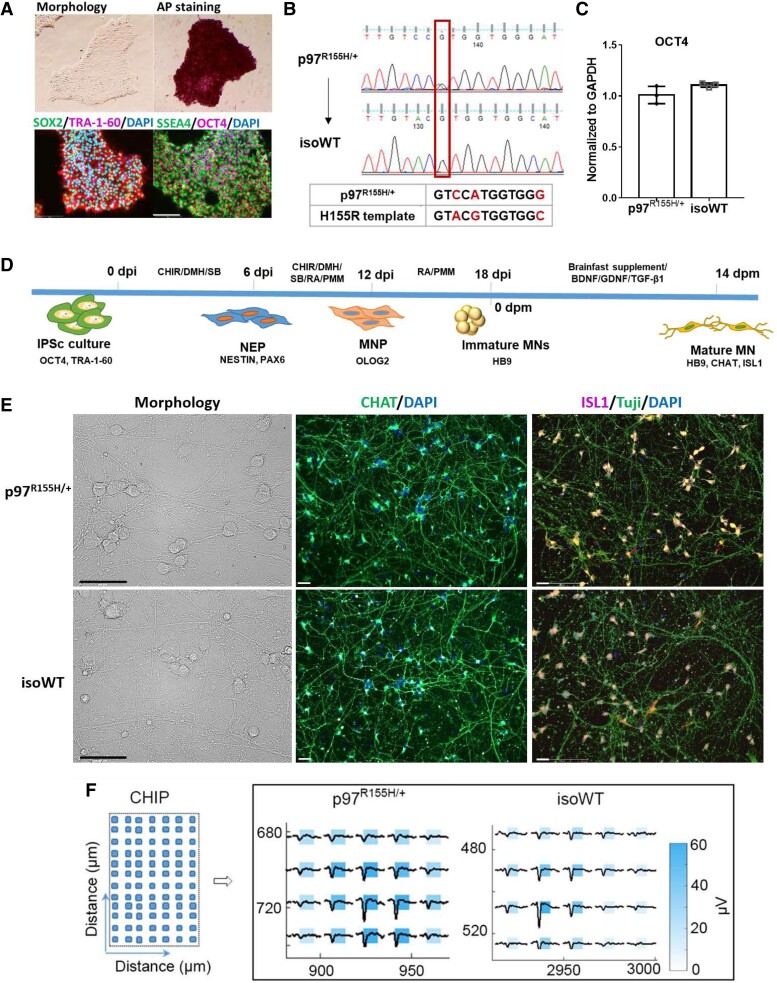
Figure 1.
Generation of ihMNs from patient-derived fibroblast cells. (A) Verification of iPSC identity in cells derived from p97R155H/+ patient cells. Scale bar indicates 200 μm. (B) Generation of isogenic lines using CRISPR/Cas9 to correct p97 R155H mutation. Two synonymous mutations were introduced in the HDR template: the C to A mutation is to remove PAM site to prevent re-cutting by Cas9 and the G to C mutation is to introduce a restriction enzyme site (ShpI) to allow us to identify presence of HDR by a restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) assay. The positive iPS clones detected by RFLP assay were further confirmed by DNA sequencing. (C) qPCR analysis of the OCT4 mRNA expression in p97R155H/+ and isoWT iPSCs. (D) Schematic showing strategy for promoting motor neuron differentiation. Days post induction (dpi) and Days post maturation (dpm). (E) Representative images of morphology and CHAT, ISL1 immunofluorescence staining in mature MNs. Scale bar indicates 50 μm. (F) Illustration of the chip used to recorded neuron activity in Maxwell (left, CHIP) and the representative footprints of spontaneous firing from a single cluster of MNs at 14 dpm. Immature MNs were seeded on chips in the Maxwell plate and incubated under maturation culture conditions. Neuron activity was recorded at 7, 10 and 14 dpm. Each square represents an electrode used to record neuron activity. The distance indicates the position of the neuron activity was recorded in the chip.