Fig. 2.
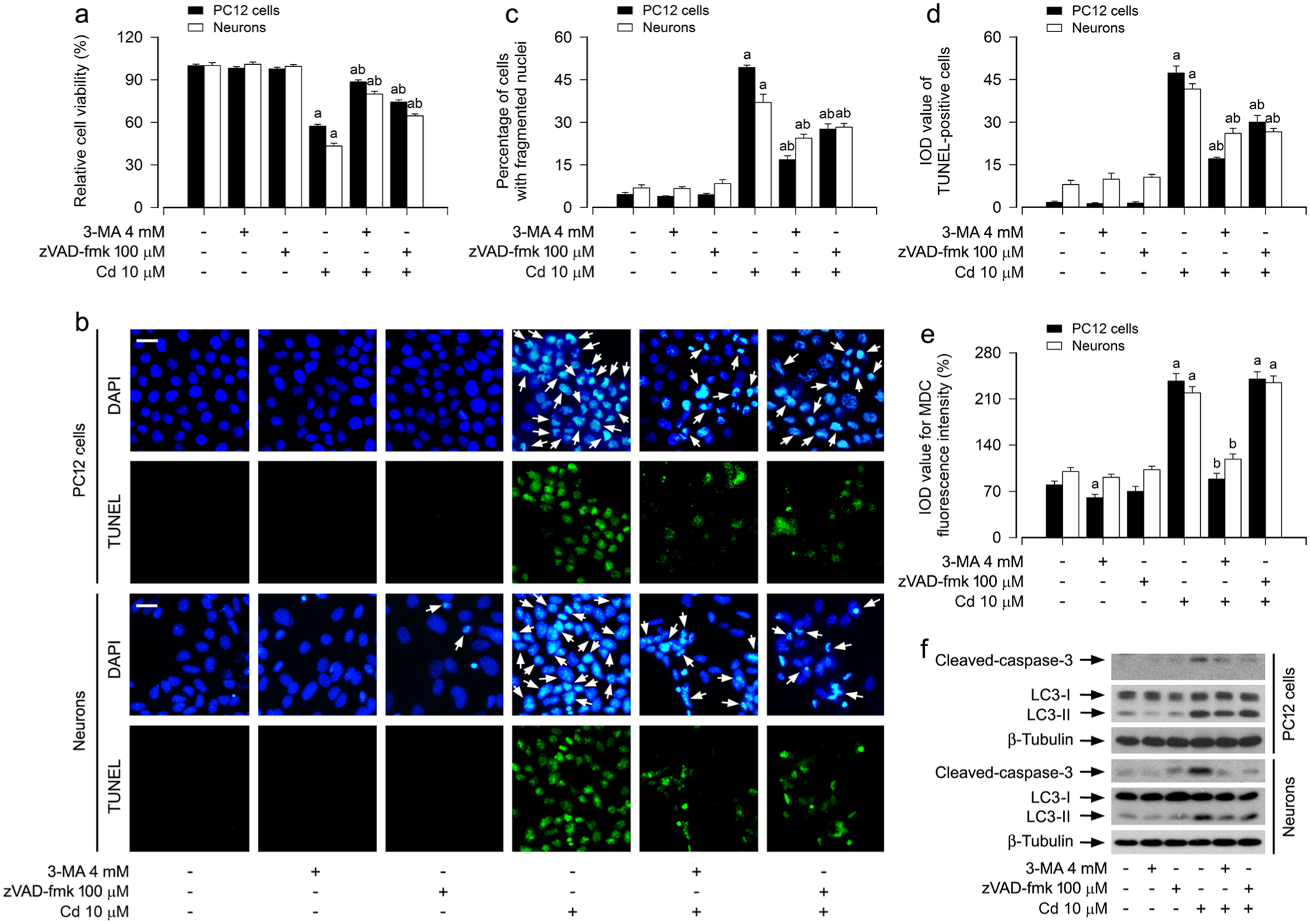
Cd elicits autophagosome expansion-dependent apoptosis in neuronal cells. PC12 cells and primary neurons were pretreated with/without 3-MA (4 mM) or zVAD-fmk (100 μM) for 1 h, followed by exposure to Cd (10 μM) for 12 h (for MDC staining, Western blotting) or 24 h (for cell viability analysis, DAPI and TUNEL staining). a The cell viability was determined by the MTS assay. b The apoptotic cells were evaluated by nuclear fragmentation and condensation (arrows) using DAPI staining (upper panel) and concurrently by in situ detection of fragmented DNA (in green) using TUNEL staining (lower panel). Scale bar: 20 μm. c, d The percentages of cells with fragmented nuclei (c) and the number of TUNEL-positive cells (d) were quantified. e The fluorescence intensity for MDC-labeled vacuoles in the cells was quantified. f Total cell lysates were subjected to Western blotting using indicated antibodies. The blots were probed for β-tubulin as a loading control. Similar results were observed in at least three independent experiments. For a, c, d and e, all data were expressed as means ± SE. n = 5, aP < 0.05, difference with control group; bP < 0.05, difference with 10 μM Cd group
