Figure 3.
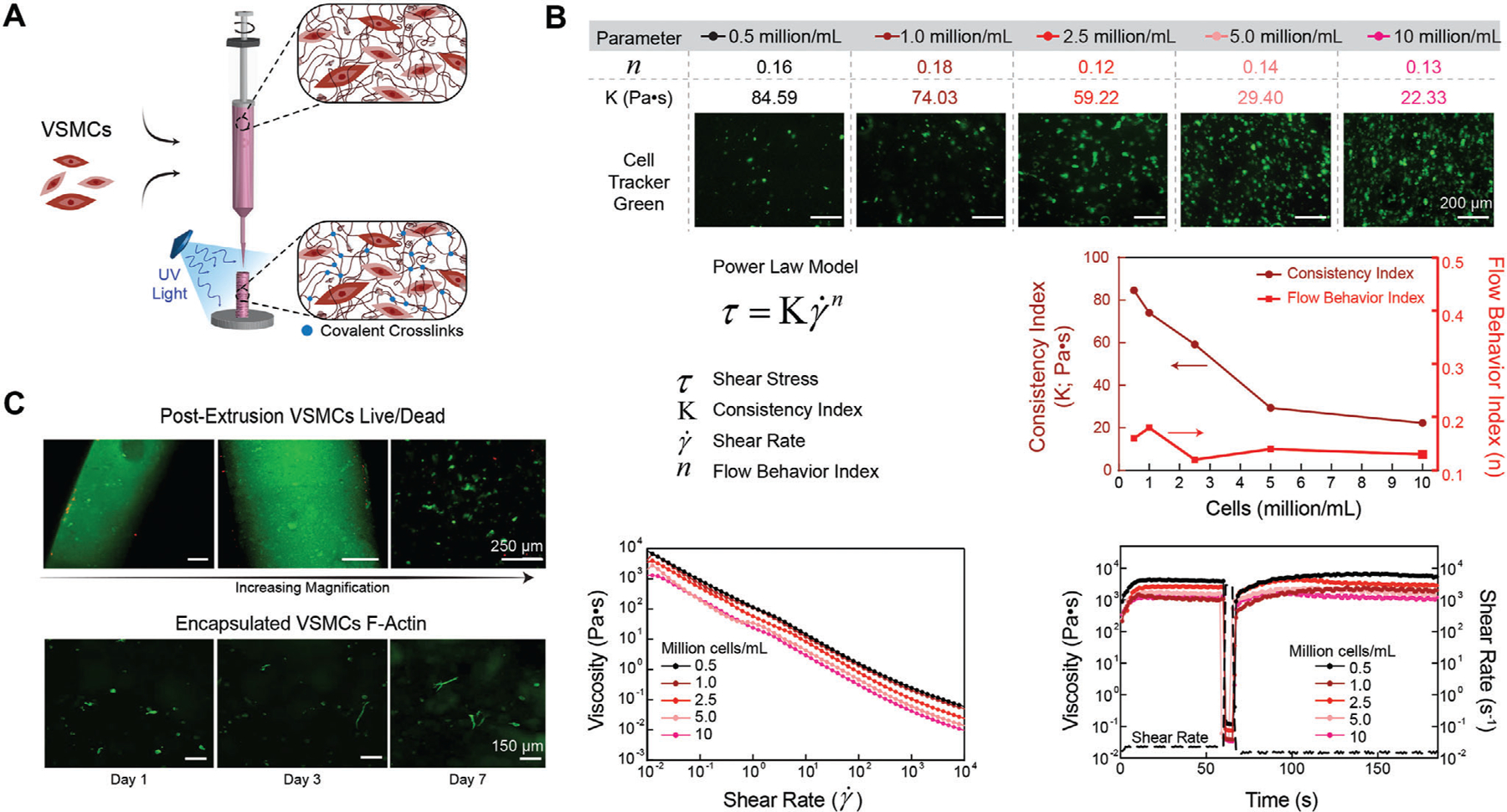
3D Bioprinting using nECM bioink. A) Schematic illustrating VSMC encapsulation and extrusion for 3D bioprinting. B) All cell densities encapsulated within the nECM maintained a high low-shear viscosity, shear thinning profile (flow behavior index < 1), and recoverability optimal for 3D bioprinting. However, as the encapsulation density was increased, the consistency index decreased in a logarithmic manner. C) Directly after extrusion, VSMCs maintained a high cell viability, illustrating an increase in magnification from left to right (top row). After crosslinking the nECM, encapsulated VSMCs demonstrate an increase in spreading and elongation between days 1, 3, and 7 (bottom row).
