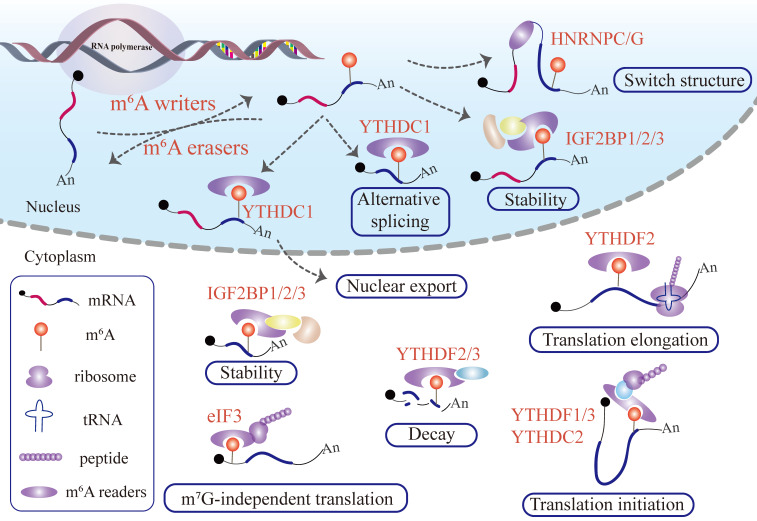
Figure 1.
Functions of m6A modification in mRNA. Writer proteins deposit m6A remarks in newborn mRNAs transcript from DNA.The m6A signal deposited in mRNA can adjust the local flanking sequences by the m6A flag installed in the mRNA and recruit YTHDC1, which manipulates mRNA alternative splicing and nuclear export. The mRNA labeling m6A can recruit IGF2BPs to stabilize the mRNA in the nucleus. After penetrating the cytoplasm, the m6A-labeled mRNA produces sophisticated and far-reaching biological effects. IGF2BP1/2/3 proteins recognize the m6A remark embedded in mRNA, influencing the mRNA stability. On the contrary, m6A deposited in mRNA can recruit YTHDF2/3, promoting target mRNA degradation. In addition, the presence of an m6A modified mRNA regulates target mRNA translation and, consequently protein synthesis. The binding of eIF3 and m6A pockets launches m7G-independent translation. The interplay between YTHDF2 and m6A sites existing in mRNA enhances translation elongation. YTHDF1/3 or YTHDC2 perceive m6A pockets, and promotes target mRNA translation initiation.