Fig. 3.
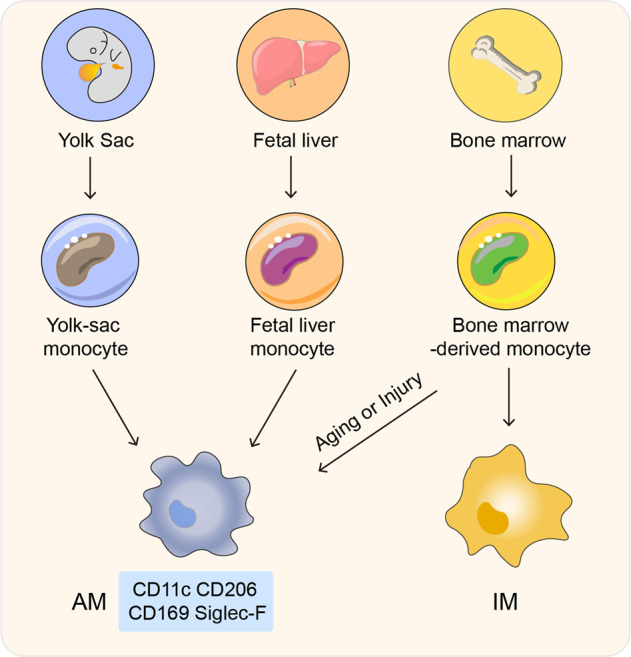
The origin of lung macrophages in mice. Lung macrophages mainly include two populations, AMs and interstitial macrophages (IMs). IMs originate from bone marrow-derived monocytes and are maintained by circulating monocytes. Unlike IMs, AMs are established prior to birth in the yolk sac, where erythromyeloid progenitors (EMP) develop at embryonic day (E) 8.5. Subsequently, progenitors migrate to the fetal liver, generating monocyte clones at E12.5. After birth, bone marrow-derived monocytes can be recruited to alveoli in aging mice or injured mice, as a supplement for AMs. In fact, in the steady-state, AMs maintain themselves by self-renewal. Murine AMs highly express CD11c, CD206, CD169, and Siglec-F
