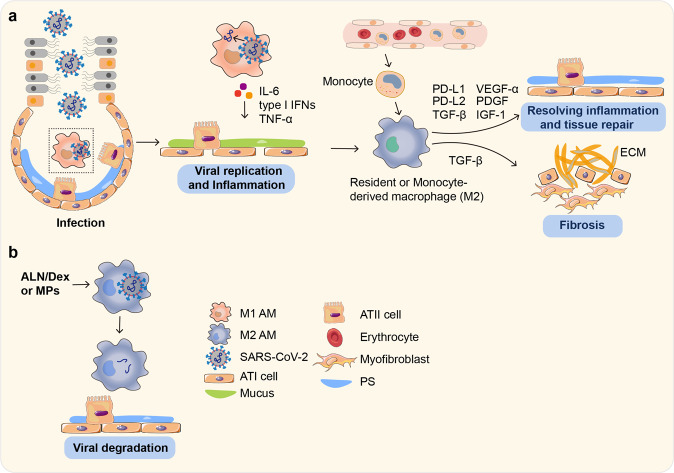
Fig. 4.
M1-like and M2-like AMs involve in SARS-CoV-2 infection differently. a M1-like AMs have more acidic endosomes than M2-like AMs, leading to release of the viral RNA from endosomes into the cytoplasm for replication. Meanwhile, proinflammatory cytokines, including TNF-α and IL-6, are upregulated in virus-infected M1 AMs, causing lung injury. Bone marrow-derived monocytes migrate into alveoli to replenish AMs during SARS-CoV-2 infection. These cells together with resident AMs may contribute to inflammation. However, they can also be polarized into potential M2-like phenotype by IL-4 and IL-13 stimulation, producing a variety of factors that facilitate tissue repair and resolving inflammation. If the process loses its balance, undesirable repair processes can cause tissue fibrosis. b Microparticles (MPs), Alendronate (ALN), and Dexamethasone (Dex) can promote viral degradation by polarizing AMs into M2 phenotype. M2-like AMs have a higher endosomal pH, which hinders CTSL activity and subsequent viral RNA release, leading to the delivery of viruses to lysosomes for degradation