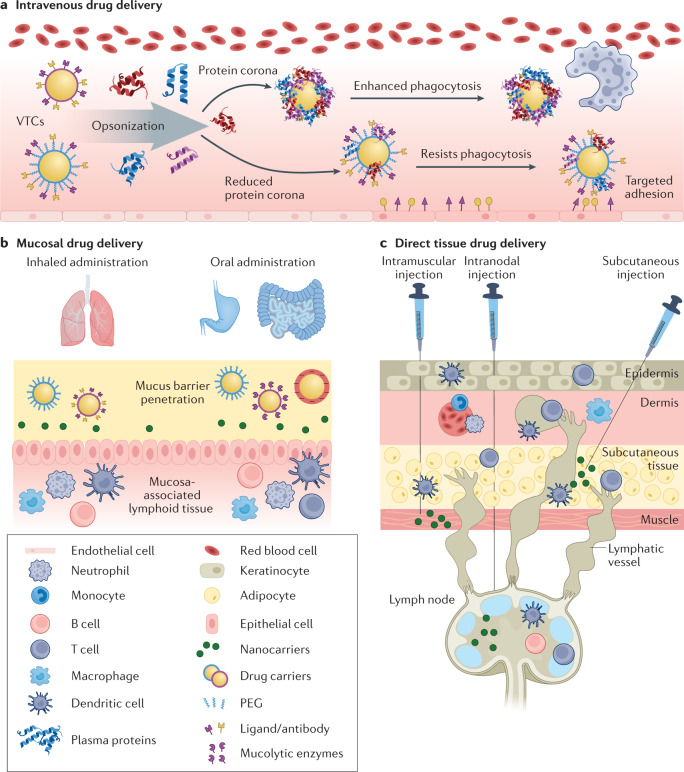
Fig. 3. Route of administration for immunomodulation.
The effectiveness of particle-based therapeutics strongly depends on the route of administration. a | Intravenous routes allow systemic delivery, but pose challenges including quick clearance and complement activation. Grafting of polyethylene glycol (PEGylation) reduces protein corona formation allowing for improved targeting and reduced clearance. b | Mucosal drug delivery allows direct targeting of inflamed tissue. Here, particles are designed to target or travel through mucous membranes of diseased tissue. c | Direct tissue drug delivery can be applied to target lymphoid tissue by intramuscular, subcutaneous or intranodal injections. VTC, vascular-targeted carrier.