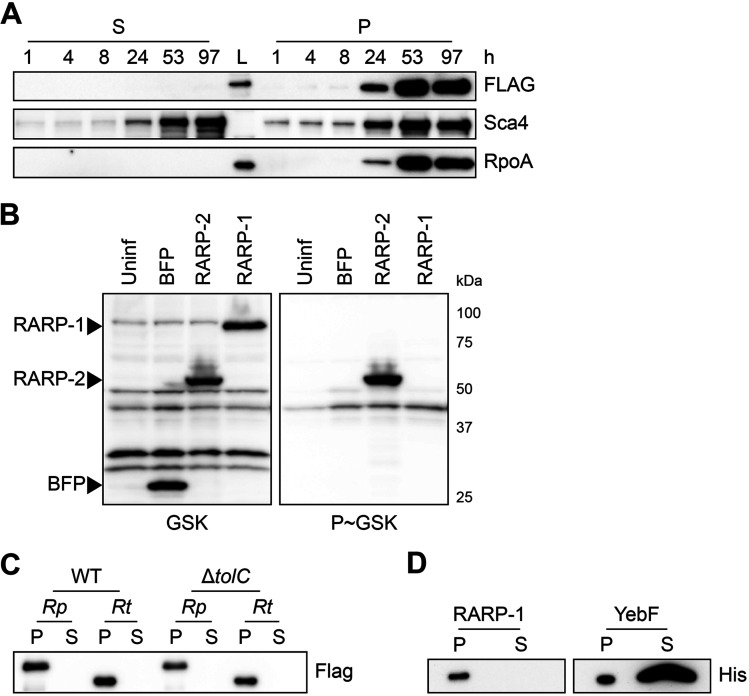
FIG 4.
RARP-1 is not secreted. (A) Western blots for FLAG (top) and Sca4 (middle) during infection of A549 cells with rarp-1::Tn + 3×FLAG-RARP-1 bacteria. Infected host cells were selectively lysed at various time points to separate supernatants (S) containing the infected host cytoplasm from pellets (P) containing intact bacteria. RpoA (bottom) served as a control for bacterial lysis or contamination of the infected cytoplasmic fraction. L, ladder. (B) Western blot for GSK-tagged constructs during infection of Vero cells. Whole-cell infected lysates were probed with antibodies against the GSK tag (left) or its phosphorylated form (P~GSK, right) to detect exposure to the host cytoplasm. BFP (nonsecreted) and RARP-2 (secreted) were used as controls. Uninf, uninfected whole-cell lysate. (C) Western blot for FLAG using N-terminal FLAG-tagged R. parkeri (Rp) or R. typhi (Rt) RARP-1 expressed by WT or ΔtolC E. coli. (D) Western blot for His using C-terminal Myc-6×His-tagged R. typhi RARP-1 or C-terminal 6×His-tagged E. coli YebF expressed by WT E. coli. For panels C and D, cultures were pelleted (P) and the culture supernatant (S) was filtered and precipitated to concentrate proteins released into the medium.