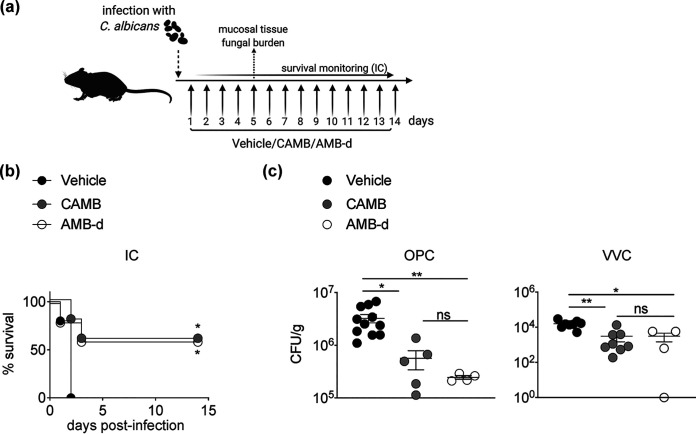
FIG 1.
Cochleated amphotericin B (CAMB) exhibits comparable efficacy with AMB deoxycholate (AMB-d) in mouse models of invasive (IC), oropharyngeal (OPC), and vulvovaginal candidiasis (VVC). (a) Mice were treated daily with CAMB via oral gavage, AMB-d intraperitoneally, or the vehicle control starting at day 1 postinfection. (b) C. albicans was injected intravenously in C57BL/6 mice and survival was monitored (n = 5 per group). (c) Act1−/− mice were infected with C. albicans in models of OPC (n = 4 to 11 per group) and VVC (n = 4 to 8 per group). At day 5 postinfection, the mice were euthanized and tongue (for OPC) or vaginal tissue (for VVC) was harvested to quantify fungal burden. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01 as determined using a log-rank test (b), one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple-comparison test (panel c, OPC), or Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn’s multiple-comparison test (panel c, VVC). Data are summary of one (b) or two independent experiments (c).