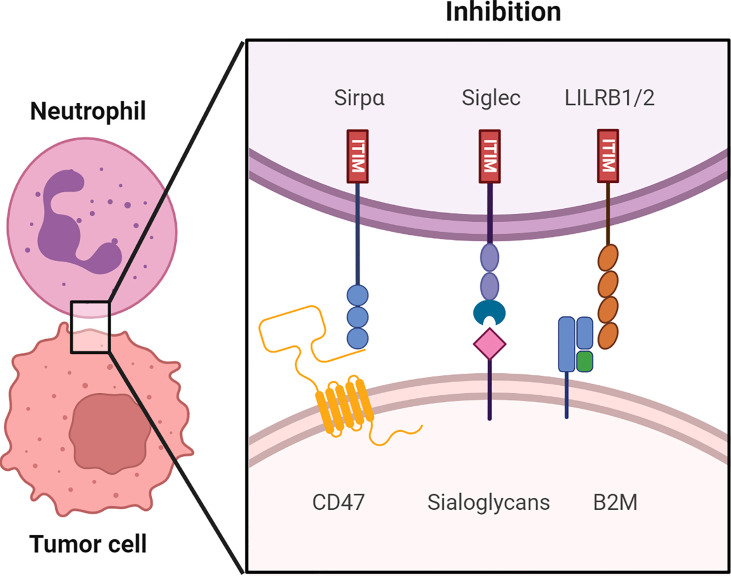
Figure 1.
An overview of putative immune checkpoints molecules regulating myeloid cell function in human tumor microenvironments (TME). Receptor-ligand interaction including the CD47-SIRPα axis, sialoglycans-Siglec axis and HLA1 (B2M)-LILRB 1/2 axis in the immune synapse between the myeloid cells, such as neutrophils and macrophages and the tumor cells. Src family kinases phosphorylate the ITIM upon binding of checkpoint molecules to their respective receptors. The following recruitment and activation of SHP-1 and SHP-2 suppresses the anti-tumor immune responses. Consequently, tumor cells are able to evade immune surveillance.