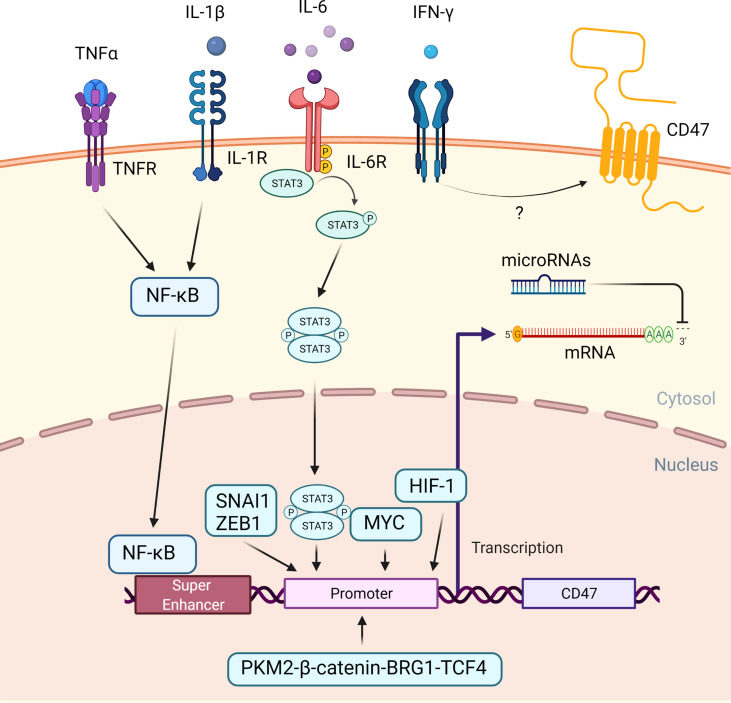
Figure 2.
Regulation of CD47 expression in cancer cells. An overview of the mechanisms that cause CD47 overexpression in cancer. When the TNF receptor and the IL-1 receptor are activated by extracellular TNF-α and IL-1, NFκB is recruited and translocated to the nucleus, where it binds to a super-enhancer to promote CD47 expression. Extracellular IL-6 induces STAT3 signaling. Phosphorylated STAT3 complex and other transcription factors, including SNAI1, ZEB1, MYC, HIF-1, PKM2-β-catenin-BRG1-TCF4 complex enhance CD47 expression by directly binding to the CD47 promotor. Extracellular IFN-γ increased the CD47 expression, albeit the exact mechanism is unknown. Subsequently, at a post-transcription level, microRNAs could bind to the 3’ untranslated region of CD47 mRNA, causing translation to be disrupted.