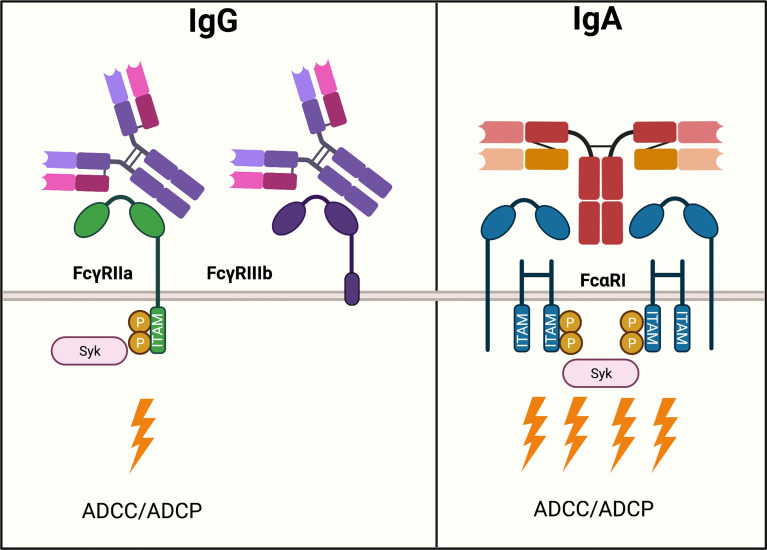
Figure 3.
IgG- and IgA-mediated activation of neutrophils. Neutrophils express various Fc receptors, the two most abundant of which, FcγRIIa and CD16b, are important in modulating activation upon IgG ligation. FcγRIIb is expressed nearly 9-fold greater than FcγRIIa. FcγRIIa is an activating receptor that binds to IgG in a 1:1 stoichiometry and signals via one ITAM motif. Downstream ITAM signaling activates effector functions such as ADCC. Moreover, neutrophils express FcγRIIb, which lacks an active intracellular signaling domain and functions as a scavenger receptor for IgG. IgA binds to FcαRI expressed on neutrophils, an activating Fc receptor in a 1:2 stoichiometry. A total of four ITAMs cause a strong activation of ADCC.