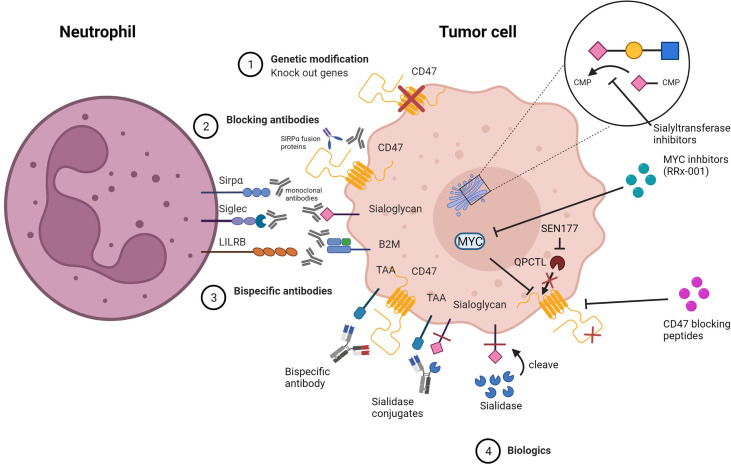
Figure 5.
Strategies for inhibiting myeloid checkpoints. 1) Genetic knock out of target genes involved in the inhibitory pathway. 2) Specific blocking of target checkpoint molecules with mAbs or soluble ligand-Fc fusion proteins to inhibit receptor binding and checkpoint axis activation. 3) Bispecific antibodies that target both TAA and checkpoint molecules simultaneously to avoid off-target side effects.4) Biologics that alter the structure of the target protein, preventing it from binding to the receptor, or that inhibit expression or block the target protein.