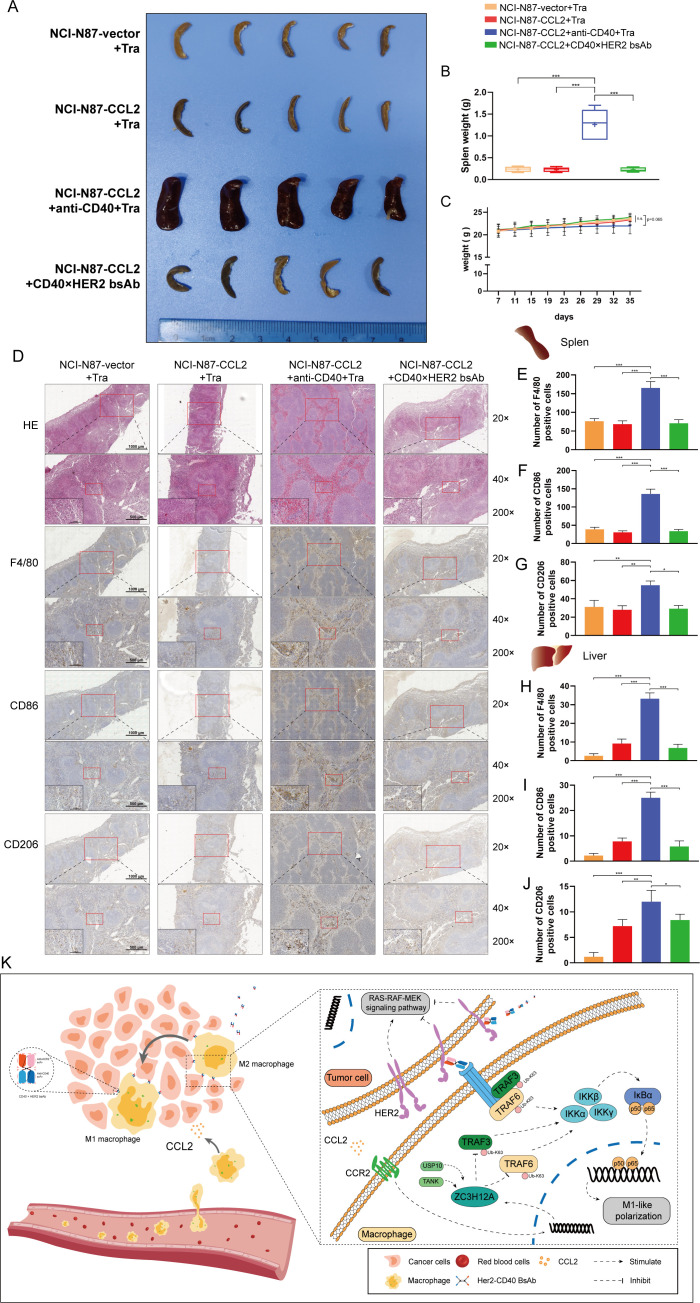
Figure 6.
CD40 ×HER2 bsAb treatment avoided irAEs. (A–C) Spleen volume images (A), spleen weight (B) and mouse body weight curves (C) of each group were presented. (D–G) H&E staining and IHC staining for F4/80, CD86, and CD206 were presented to show the infiltrating macrophages in mouse spleen tissues (D). IHC scores for F4/80 (E), CD86 (F) and CD206 (G) were statistically analyzed. (H–J) IHC staining in mouse liver tissues for F4/80, CD86, and CD206 was performed. IHC scores for F4/80 (H), CD86 (I) and CD206 (J) were statistically analyzed in mouse liver tissues. (K) Schematic diagram: Tumor cell-derived CCL2 decreased M1-like phenotype of TAMs via ZC3H12A-TRAF6/3 signaling, whereas CD40 markedly protected the TRAF6/3 from K63-linked deubiquitination, thereby reactivating the NF-κB signaling. CD40 ×HER2 bsAb had the CD40 targeted macrophages costimulatory activity and a HER2-mediated antitumor activity, with absence of irAEs, which overcame trastuzumab resistance in GC. n=5 per group. tra, trastuzumab treatment. Scale bar, ×20, 1000 µm; ×40, 500 µm; ×200, 100 µm. *P<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001. bsAb, bispecific antibody; GC, gastric cancer; IHC, immunohistochemistry; irAEs, immune-related adversary effects.