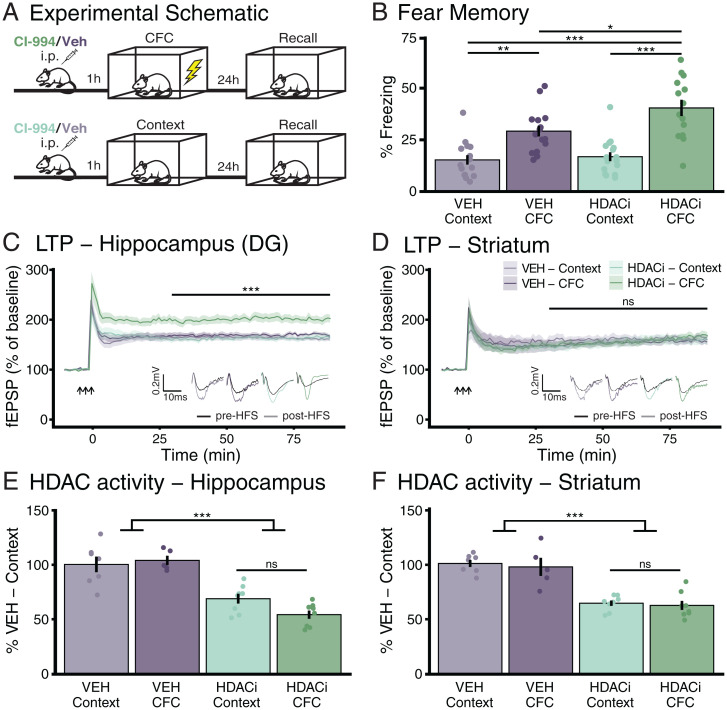
Fig. 1.
HDACi treatment enhances contextual fear memory formation and hippocampal, but not striatal LTP, despite reducing HDAC activity in both brain regions. (A) Schematic of the experimental outline. (B) HDACi combined with CFC increases the percent of time spent freezing (>1 s) during 3-min reexposure to the conditioning chamber 24 h after conditioning. n (VEH-Context) = 15; n (VEH-CFC and HDACi-Context) = 16; n (HDACi-CFC) = 14. (C and D) HDACi combined with CFC enhances LTP in response to HFS in the perforant pathway of the DG (C) but not in cortico-striatal fibers (D) 1 h after conditioning. Statistical differences were calculated from 30 min (end of short-term potentiation) to end of recording. n = 8 animals per group. (E and F) HDAC activity was reduced after HDACi in both the hippocampus (E) and striatum (F) with no further reduction in HDAC activity in response to CFC. Hippocampus and striatum: n (VEH-Context) = 7; n (VEH-CFC) = 5; n (HDACi-Context and CFC) = 8. One or two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s HSD. Graphs represent mean ± SEM, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001; ns, not significant.