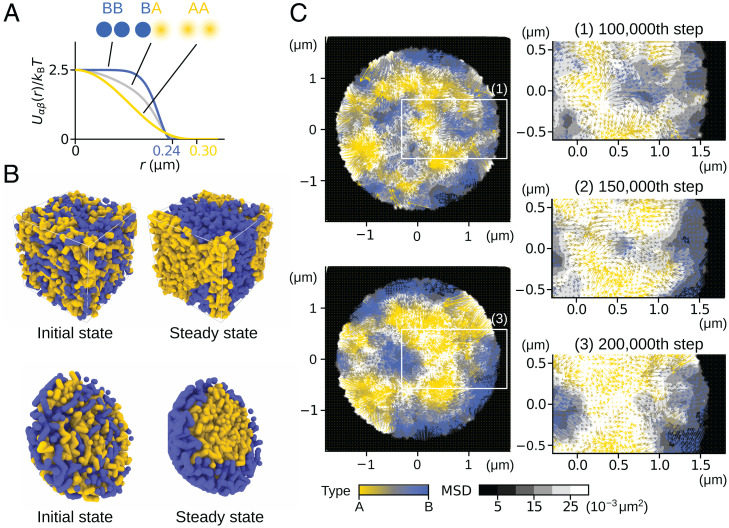
Fig. 3.
Heterogeneous repulsive interactions and phase separation. (A) Potential functions between type-A, type-B, or type-u regions in distance r; , and . (B and C) A polymer-blend system was simulated to demonstrate the phase separation induced by heterogeneous repulsive interactions; 100 chains, each composed of 20 segments of type-A (yellow), and 100 chains, each composed of 20 segments of type-B (blue), were mixed and subjected to the Brownian motion. (B) Polymer chains mixed in a box with the periodic boundary condition (Top) and in a spherical container shown with the semisphere view (Bottom). (Left) The initial configuration. (Right) A snapshot after the system reached a steady state. (C) (Left) Cross-section of the sphere at the th step (Top) and the th step (Bottom). (Right) Close-up views of the rectangular areas in Left. Fluctuation (gray-scaled background, the 10-step MSD) and flow (arrow, the 10-step displacement) of polymer segments averaged within each 0.12-m region around the mesh points are shown. Colors of flows represent the ratio of A/B density. The images were rendered using OVITO (43).