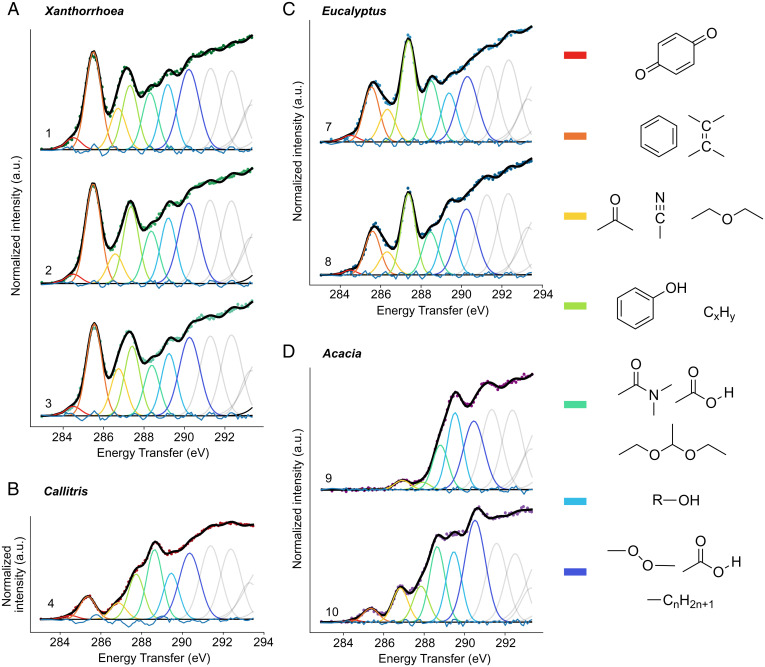
Fig. 1.
XRS carbon K-edge spectra decomposition. (A) 1, X. arborea; 2, X. semiplana ssp. tateana; 3, X. semiplana. (B) 4, C. calcarata. (C) 7, white mallee; 8, E. largiflorens. (D) 9, Acacia sp.; 10, A. bakeri. For comparison of the samples’ chemistry in a semiquantitative way, we performed a decomposition of the normalized spectra. The centers of Gaussians correspond to core electron transitions at specific functional groups as reported in the literature of soft X-rays absorption and/or EELS studies (SI Appendix, Table S2). For the interpretation of the XRS data only the transitions of core electrons to bound unoccupied states (i.e., preedge transitions) up to approximately 291.5 eV were used. Above that limit, there is contribution from highly delocalized excited states (i.e., 1s–σ* transitions) and overlapping contribution of Feshbach resonances.