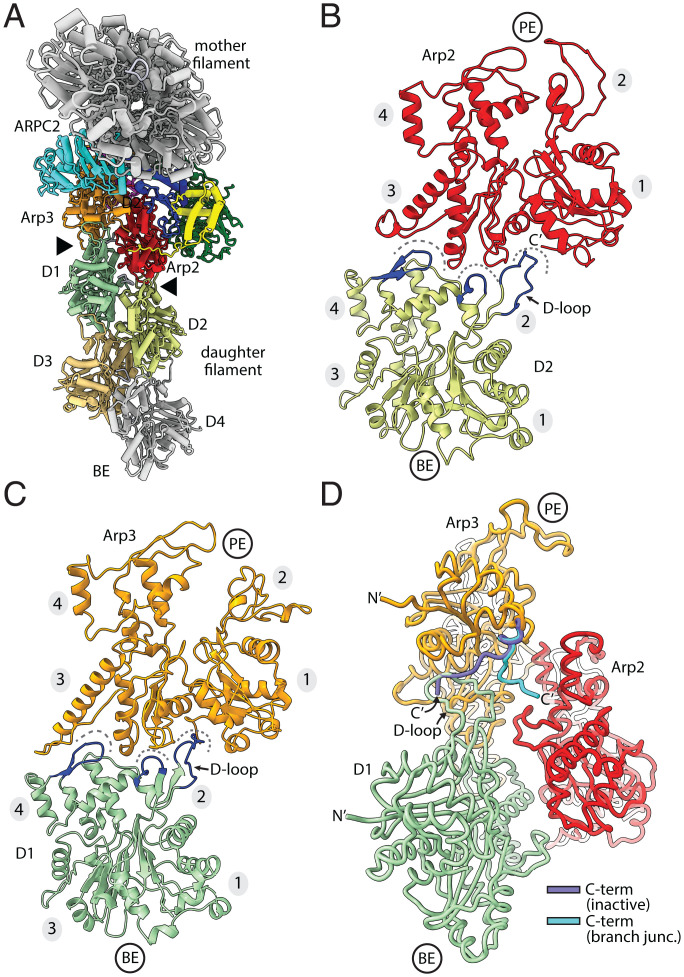
Fig. 3.
Contacts of Arp2/3 complex with the daughter filament of actin. (A) Ribbon representation of the branch junction looking down the helical axis of the mother filament. This view highlights the daughter filament-Arp2/3 complex interface (black arrowheads). (B and C) Long pitch (intrastrand) interactions between each Arp and actin subunits in the daughter filament. Dashes indicate three seams at the barbed end of each Arp that accept key structural protrusions (blue) from the pointed end of the actin subunits. Subdomains in actin and Arps are numbered 1 to 4 in this figure and throughout. (D) Diagram showing the position of the Arp3 C-terminal tail in the present branch junction model versus its position in the inactive Arp2/3 complex. The inactive C-terminal tail was modeled by overlaying Arp3 in 4JD2 onto subdomains 1 and 2 of Arp3 in the branch junction structure.