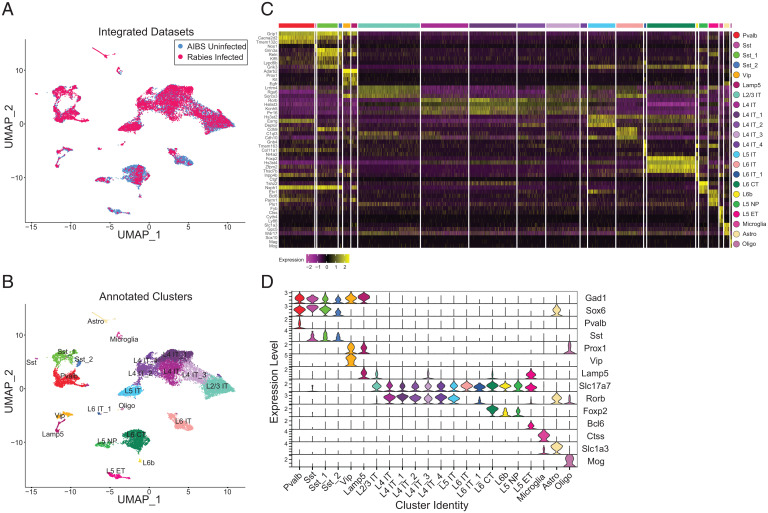
Fig. 2.
Rabies-infected nuclei can be transcriptomically classified de novo despite changes in gene expression. (A) UMAP of 8,745 rabies-infected nuclei (red) and 9,508 AIBS uninfected control nuclei (blue) after anchor-based data integration. (B) UMAP of anchor-based integrated rabies-infected and AIBS uninfected control nuclei colored by de novo cell subclass annotations. (C) Heatmap showing normalized and scaled expression level of DEGs for each cluster in B compared with all other clusters. Clusters are color coded according to B and delineated by white vertical lines. (D) Violin plots illustrating normalized expression level of canonical marker genes for each cluster, which are composed of both infected and AIBS uninfected control nuclei.