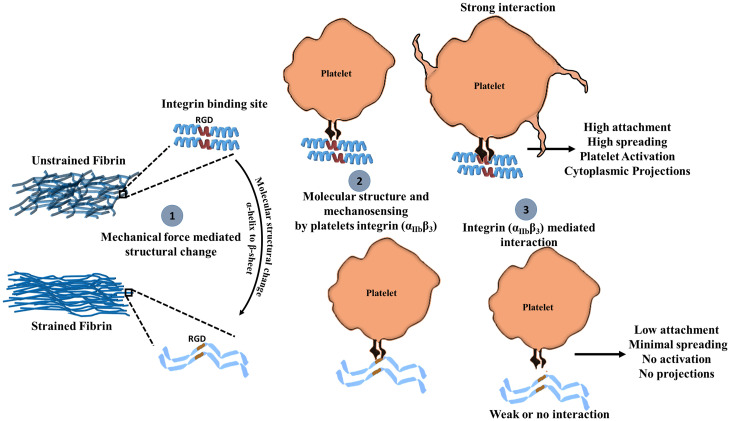
Fig. 5.
Proposed mechanism for mechano-chemical platelet activation on fibrin. (1) Mechanical force promotes molecular structural changes in fibrin. (2) Platelet integrin αIIbβ3 binds to unstrained fibrin RGD domains in the helical coiled-coil region of fibrin more effectively than to sheets in the same region, which leads to (3) increased platelet attachment, spreading, and activation.