Figure 6.
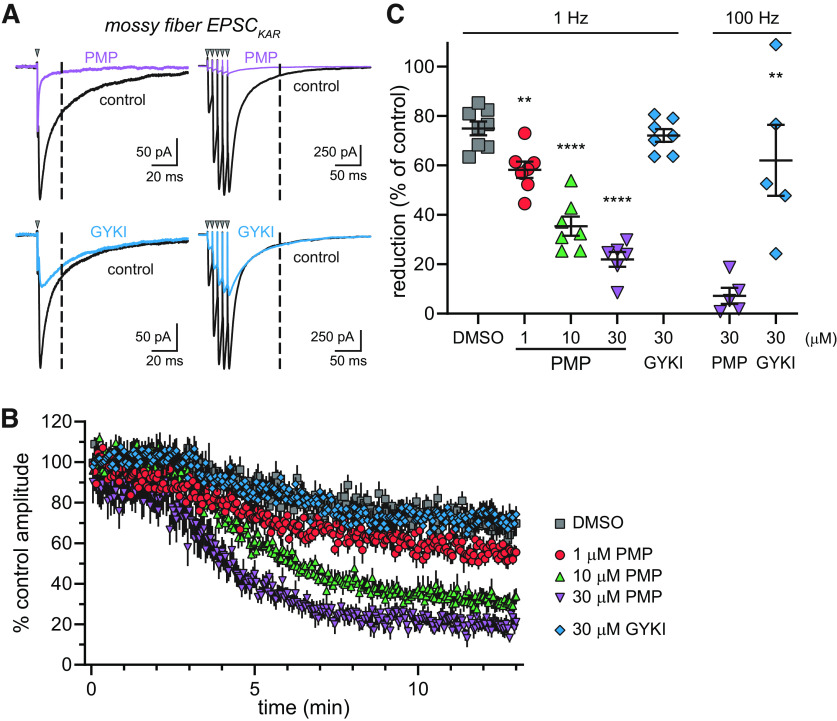
KARs at mossy fiber CA3 pyramidal cell synapses are inhibited by PMP. A, Representative EPSCKAR recorded at mossy fiber synapses in control conditions (black lines) or those in the presence of 30 µm PMP (purple line) or 30 µm GYKI-53655 (blue line). Synaptic currents were evoked by stimulation of the stratum lucidum at 1 Hz (left) or with 5 stimuli at 100 Hz (right). NBQX (0.5 µm) was present during EPSCKAR recording at 1 Hz but not 100 Hz. The amplitude of EPSCKARs were measured at 20 ms after the peak of the mixed AMPAR/KAR EPSC during 1 Hz stimulation or 100 ms after the last peak current following 100 Hz stimulation (dashed lines). PMP inhibited both AMPA and kainate receptor components, whereas GYKI-53655 only had an effect on AMPA receptors. B, time course changes of the percentage amplitude of EPSCKAR in response to PMP, GYKI-53655, or DMSO application. Current amplitudes were normalized to the mean amplitudes of first 20 EPSCKAR. DMSO was applied as a control for run down of the currents. The time course of EPSCKAR amplitudes in the presence of DMSO and GYKI-53655 overlap, whereas PMP produced concentration-dependent inhibition. C, Summary data showing the mean, SE, and data from individual recordings for the percentage inhibition of EPSCKAR by PMP after 10 min of application. Significance indicated as **p < 0.01 and ****p < 0.0001 compared with DMSO-treated group (1 Hz) or the amplitudes of EPSCKAR in the presence of GYKI-53655 compared with PMP (100 Hz).