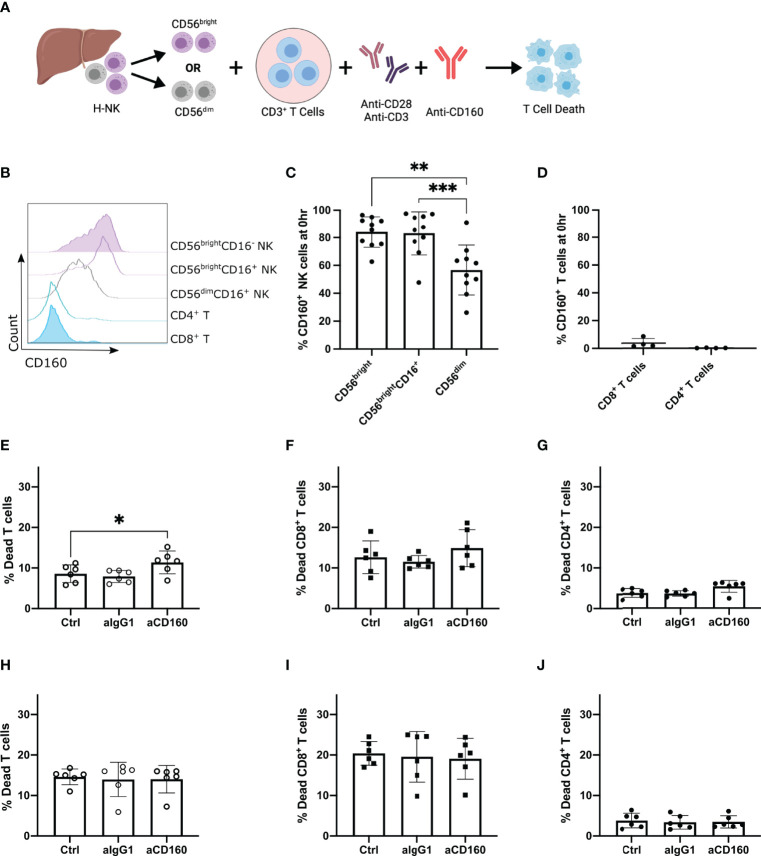
Figure 5.
Agonistic anti-CD160 mAb acts on hepatic CD56bright NK cells to enhance their killing of allogenic T cells. Activated CD3+ T cells co-cultured with H-NK cells or FACS-sorted hepatic CD56brightCD16+/- or CD56dimCD16+ NK cells with or without a mAb against CD160 for 24 hr (n = 6-10). (A), Schematic of experimental design (B), Representative flow plot of CD160 expression on NK and T cell populations at 0 hr prior to coculture. ‘Ctrl’ indicates cocultures of CD3+ T cells with the specified H-NK cell subset without the addition of any antibody. ‘aIgG1’ indicates cocultures of CD3+ T cells with the specified H-NK cell subset with the addition of an IgG1 antibody. ‘aCD160’ indicates cocultures of CD3+ T cells with the specified H-NK cell subset with the addition of an anti-CD160 mAb. (C, D), Percent CD160 expression on NK cell (C) and T cell (D) subsets at 0 hr. (E–G), Percent dead total T cells (E), CD8+ T cells (F) and CD4+ T cells (G) following 24 hr co-culture of CD3+ T cells and CD56brightCD16+/- hepatic NK cells. (H–J), Percent dead CD56-CD19- cells (H), CD8+ T cells (I) and CD4+ T cells (J) following 24 hr co-culture of CD3+ T cells with hepatic CD56dimCD16+ NK cells. Data analysed using a repeated measures One Way ANOVA test (C–J). * p< 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001.