Figure 6.
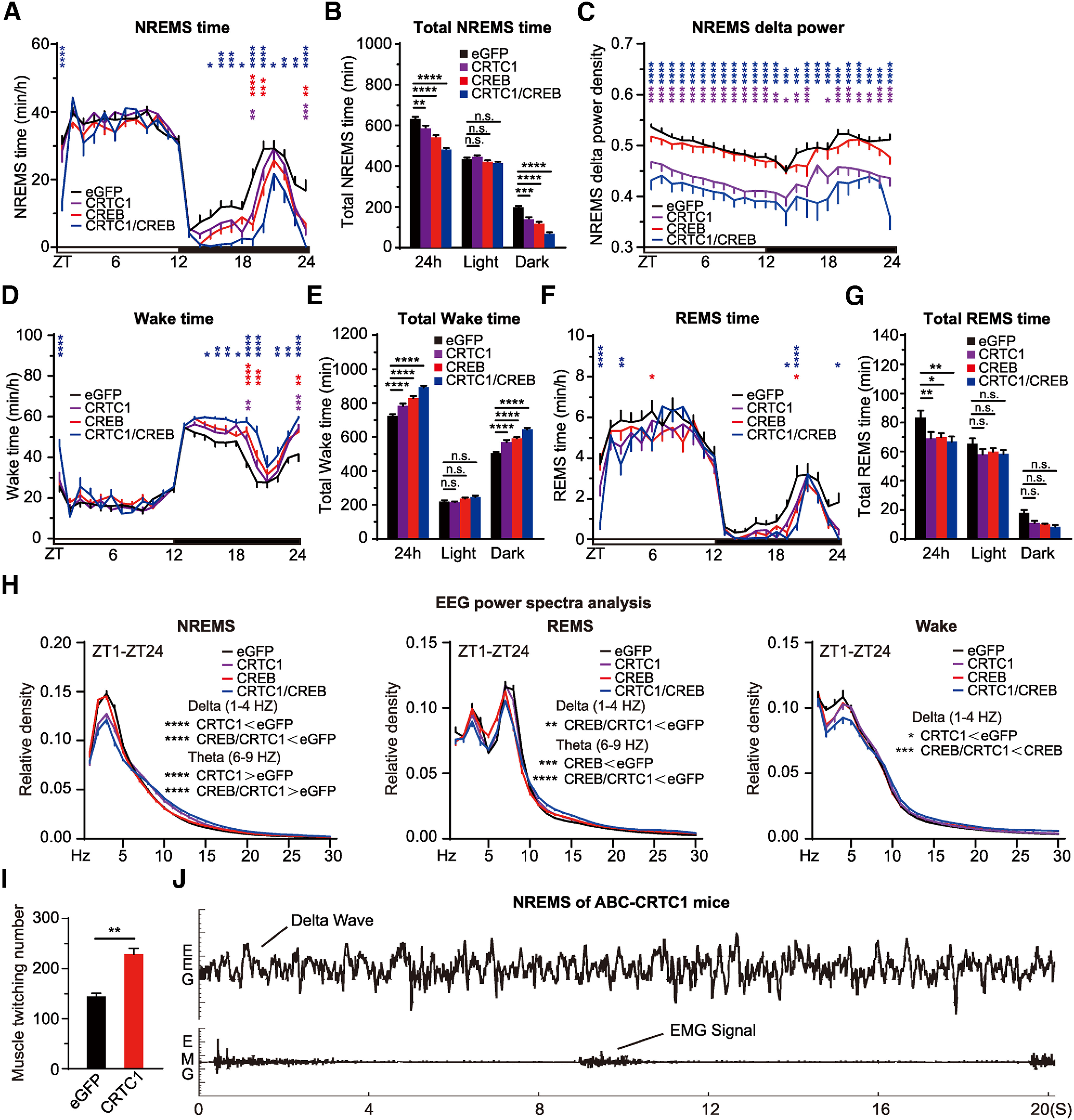
ABC-expression of CREB and/or CRTC1 reduces NREMS amount and δ power. A–C, Hourly plot of NREMS time (A), quantification of total NREMS time (B), and hourly plot of NREMS δ power (C) in the ABC-eGFP (n = 12), ABC-CRTC1 (n = 15), ABC-CREB (n = 15), and ABC-CRTC1/CREB (n = 12) mice. Shown above are statistical analysis for comparison between ABC-CRTC1 (purple*), ABC-CREB (red*), or ABC-CRTC1/CREB (blue*) mice and control ABC-eGFP mice. D–H, Hourly plots of Wake (D) or REMS (F) time, quantification of total Wake (E) or REMS (G) time, and EEG power spectra analysis of NREMS, REMS, and Wake states (H) in ABC-eGFP (n = 12), ABC-CRTC1 (n = 15), ABC-CREBΔ (n = 15), and ABC-CRTC1/CREBΔ (n = 12) mice. Shown above is the statistical analysis for comparison between ABC-CRTC1 (purple*), ABC-CREBΔ (red*), or ABC-CRTC1/CREBΔ (blue*) mice and control ABC-eGFP mice. I, Quantification of muscle twitching episodes of ABC-eGFP and ABC-CRTC1 mice during NREMS. J, Representative EEG/EMG hypnogram depicting frequent muscle twitching during NREMS in the ABC-CRTC1 mice. Data are mean ± SEM. A–H, Two-way ANOVA with Dunn's multiple comparisons test. I, Unpaired t test. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001. For the muscle twitching phenotype of ABC-CRTC1 mice during sleep, see Movie 3.
