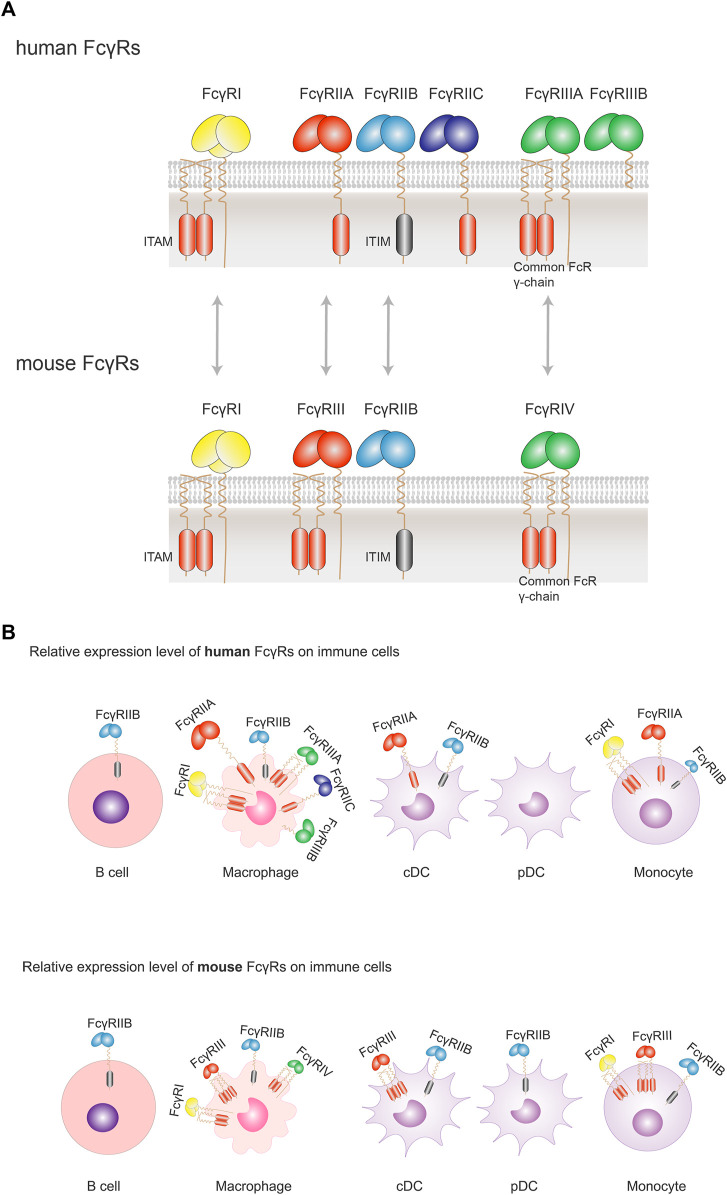
FIGURE 3.
Orthologous pairs of FcγRs between human and mouse and their cellular expression. (A) In human, three groups of FcγRs have been described: FcγRI, FcγRIIA/B/C, FcγRIIIA/B. Orthologous pairs identified in mouse include human FcγRI and mouse FcγRI, human FcγRIIA and mouse FcγRIII, human FcγRIIB and Mouse FcγRIIB, and human FcγRIIIA and mouse FcγRIV. All activating FcγRs, except FcγRIIIB, are associated with an immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif (ITAM) either in the intracellular domain (FcγRIIA and FcγRIIC) or associated with the common FcRγ chain (FcγRI and FcγRIIIA). There is only one inhibitory FcγR (FcγRIIB) in human or mouse. FcγRIIB contains an immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory motif (ITIM) in the intracellular domain. (B) FcγRs are expressed solely or simultaneously at the membrane of the various immune cells. FcγRI, FcγRIIA/B and FcγRIIIA are found on macrophages; FcγRIIA/B on conventional DC (cDC), and FcγRIIB (the sole FcγR expressed) on B cells. When co-expressed, activating FcγRs generally expressed more abundantly with respect to the inhibitory FcγRIIB. Despite a similar expression profile of FcγRs in human and mouse, there are some differences between the two species: FcγRIIB is not expressed on human pDCs, but on mouse pDCs; while co-expressed on the same cells, the inhibitory FcγRIIB is relatively less than activating FcγRs in human, which is not so apparent in mouse. Size of symbols of FcγRs is drawn to reflect their relative expression levels.