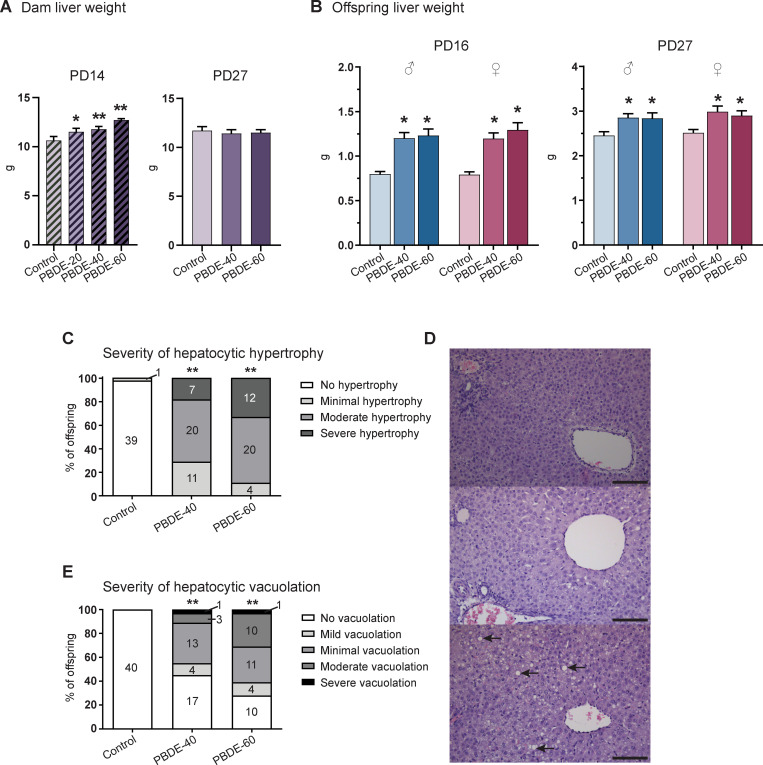
Fig 4. Effects of DE-71 exposure from GD7-PD14/16 on dam and pup liver weights and histology.
(A) Dam liver weights were increased dose-dependently in Study 1 on PD14, while there were no effects on PD27 in Study 2. n = 7 in Study 1, n = 19–21 in Study 2. Mean + SEM. (B) Male and female pup liver weights PD16 and PD27. n = 17–21. Mean + SEM. (C) Severity of hepatocytic hypertrophy in male and female offspring PD16. Centrilobular hypertrophy was observed in all exposed animals. Number of assessed offspring shown in each bar. n = 36–40. (D) Male PD16 liver from control (top), high-dose presenting with severe centrilobular hepatocytic hypertrophy (middle) and high dose with moderate hepatocytic vacuolation (bottom). Arrows show examples of large macrovesicular vacuoles in hepatocytes (E) Severity of hepatocytic vacuolation in male and female offspring PD16. Significantly increased incidence of vacuolation was seen in exposed offspring. Number of assessed offspring shown in each bar. n = 36–40. *p<0.05, **p<0.01. Scalebar = 100 μm. PBDE: polybrominated diphenyl ethers (DE-71), PD: postnatal day.