Figure 4.
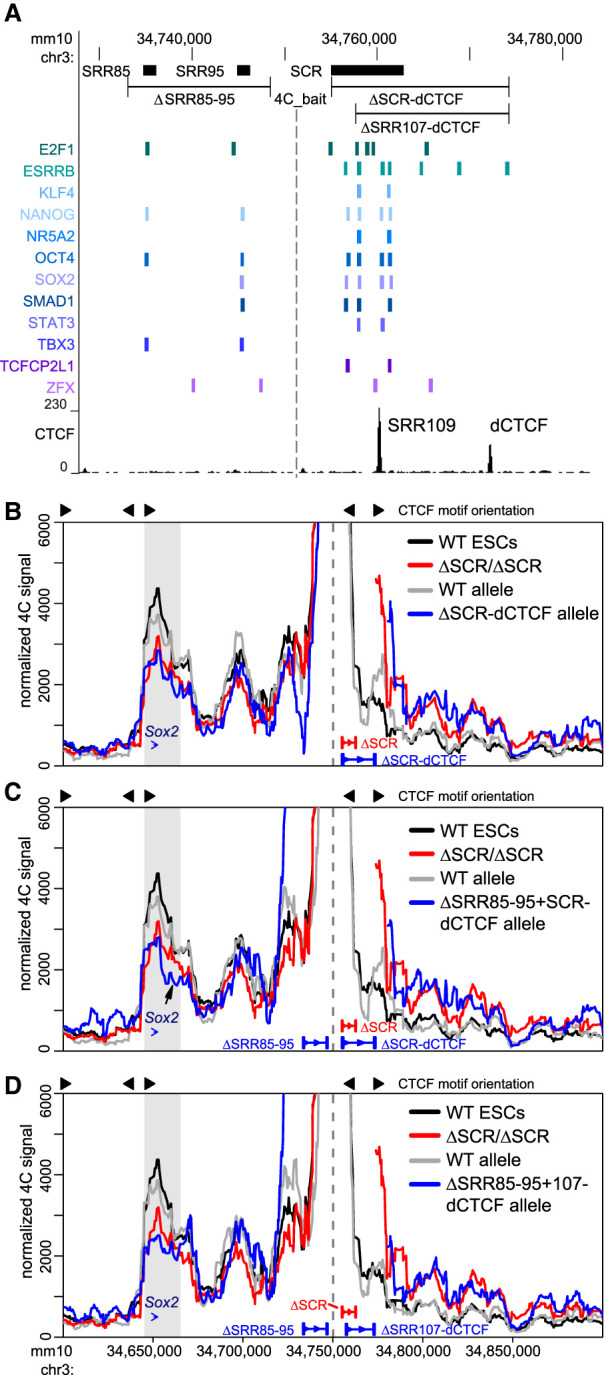
Additional CTCF- and transcription factor-bound regions surrounding the SCR support the interaction between the SCR-proximal region and the Sox2 gene. (A) The transcription factor-bound regions surrounding the SCR are displayed on the UCSC genome browser (mm10). Sox2 regulatory regions (SRRs) and the SCR (top) correspond to transcription factor-bound regions derived from ESC ChIP-seq data sets compiled in the CODEX database (bottom). (Bottom) CTCF ChIP-seq conducted in ESCs is shown, and the distal CTCF (dCTCF)-bound region is marked. In B–D, 4C data are shown for wild-type cells (WT, black, n = 4), homozygous ΔSCR/ΔSCR cells (red, n = 4), and heterozygous deletion-carrying cells (gray/blue, n = 2 for each allele). Heterozygous deletions of the SCR to dCTCF (B), SRR85 to SRR95 and SCR to dCTCF (C), or SRR85 to SRR95 and SRR107 to dCTCF (D) are shown in blue, with the WT allele shown in gray. In each panel, the dashed line indicates the location of the 4C bait region. The gray box indicates the bait-interacting region surrounding the Sox2 gene. Compared with WT cells, a significant decrease in relative interaction frequency of the 4C bait region with the Sox2 gene was observed for ΔSCR-dCTCF/+ (P = 0.006), ΔSRR85–95+SCR-dCTCF/+ (P = 0.005), or ΔSRR85–95+107-dCTCF/+ (P = 0.01) cells. In C, the arrow indicates a loss of interaction downstream from the Sox2 gene after deletion of ΔSRR85–95+SCR-dCTCF/+. For deletion alleles, the 4C signal has been omitted from the deleted region and flanking positions that are also affected by the deletion when computing running means.
