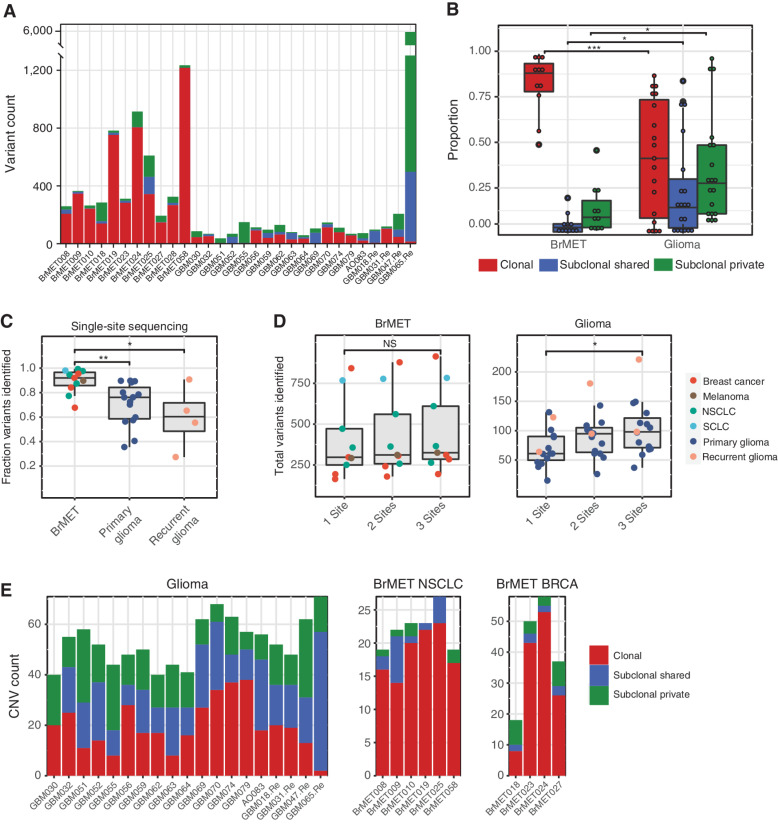
Figure 2.
Intratumoral genomic heterogeneity of variants and CNAs. A, Variant clonality per tumor. B, Proportion of clonal, subclonal shared, and subclonal private variants in brain metastases and gliomas. Significance determined by unpaired t test. *, P < 0.05; ***, P < 0.001. C, Proportion of total identified variants that would have been captured through the sequencing of a random single site from within each tumor. Significance determined by unpaired t test. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01. D, Total variants identified per tumor if one, two, or three samples were pooled for analysis. Significance determined by unpaired t test. *, P < 0.05. NS, not significant. E, CNV clonality per tumor in the gliomas (left), NSCLC brain metastases (middle), and breast cancer brain metastases (right) cohorts.