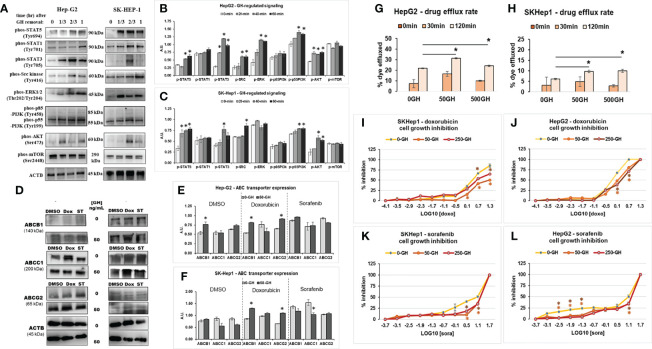
Figure 4.
GH signaling drives drug resistance in human HCC cells. (A) Treatment with exogenous GH (50ng/mL) causes activation of STATs 3 and 5, SRC family kinase, ERK1/2 and PI3K-AKT signaling in human HCC cells - Hep-G2 (B) and SK-Hep-1 (C) cells in culture. (D) Doxorubicin or sorafenib tosylate (ST) and/or GH treatment increases ABCB1, ABCC1 and ABCG2 protein expression in human HCC cells – Hep-G2 (E) and SK-Hep-1 (F) in culture. (G, H) Recombinant human GH treatment (at 50 or 500ng/mL) increases drug efflux rate in human HCC cells. (I–L) Recombinant hGH (at 50 or 250ng/mL) suppresses doxorubicin induced growth inhibition in SK-Hep-1 (I) and Hep-G2 cells (J) and sorafenib induced growth inhibition in SK-Hep1 (K) and Hep-G2 cells (L). (*p < 0.05, Students t test, n = 3).